Clinical and In Vitro Safety of Heyndrickxia coagulans AO 1167B: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial
- PMID: 39770785
- PMCID: PMC11677179
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms12122584
Clinical and In Vitro Safety of Heyndrickxia coagulans AO 1167B: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial
Abstract
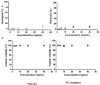
(1) Background: Heyndrickxia coagulans, a lactic acid-producing bacterium, displays characteristics of both Lactobacillus and Bacillus genera. Clinical evidence suggests its potential health benefits. This study evaluated the safety of H. coagulans AO1167B as a candidate probiotic supplement. (2) Methods: Strain identification was confirmed through morphological, cultural, and genomic analyses, including 16S RNA and whole genome sequencing to assess antimicrobial resistance and virulence factors. Phenotypic tests, such as disk diffusion for antimicrobial resistance, and safety assays for cytotoxicity and hemolytic activity, were conducted. In a phase I, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial, healthy adults were randomized into H. coagulans AO1167B and placebo groups for 60 days. Daily capsule consumption was monitored through clinical and hematological evaluations, adverse event tracking, and health surveys. (3) Results: The genome of H. coagulans AO1167B revealed no concerning features. Disk diffusion tests showed no antimicrobial resistance. The strain exhibited no cytotoxic or hemolytic activity, indicating in vitro safety. No significant differences in clinical or hematological parameters were observed between groups. The most common adverse event, gas, diminished over time. (4) Conclusions: H. coagulans AO1167B demonstrates a suitable safety profile, genetic stability, and probiotic potential for gastrointestinal health, justifying further clinical research.
Keywords: Heyndrickxia coagulans; clinical trial; humans; probiotic; randomized; safety.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hammer B.W. Bacteriological studies on the coagulation of evaporated milk. Iowa Agric. Exp. Stn. Res. Bull. 1915;19:119–131.
-
- Gupta R.S., Patel S., Saini N., Chen S. Robust demarcation of 17 distinct Bacillus species clades, proposed as novel Bacillaceae genera, by phylogenomics and comparative genomic analyses: Description of Robertmurraya kyonggiensis sp. nov. and proposal for an emended genus Bacillus limiting it only to the members of the Subtilis and Cereus clades of species. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020;70:5753–5798. - PubMed
-
- Andreoletti O., Budka H., Buncic S., Colin P., Collins J.D., De Koeijer A., Griffin J., Havelaar A., Hope J., Klein G., et al. The maintenance of the list of QPS microorganisms intentionally added to food or feed—Scientific Opinion of the Panel on Biological Hazards. EFSA J. 2008;6:923. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2008.923. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

