Unexpected Genetic Diversity of Nostocales (Cyanobacteria) Isolated from the Phyllosphere of the Laurel Forests in the Canary Islands (Spain)
- PMID: 39770827
- PMCID: PMC11676812
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms12122625
Unexpected Genetic Diversity of Nostocales (Cyanobacteria) Isolated from the Phyllosphere of the Laurel Forests in the Canary Islands (Spain)
Abstract
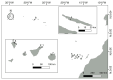
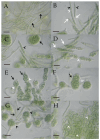
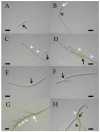
A total of 96 strains of Nostocales (Cyanobacteria) were established from the phyllosphere of the laurel forests in the Canary Islands (Spain) and the Azores (Portugal) using enrichment media lacking combined nitrogen. The strains were characterized by light microscopy and SSU rRNA gene comparisons. Morphologically, most strains belonged to two different morphotypes, termed "Nostoc-type" and "Tolypothrix-type". Molecular phylogenetic analysis of 527 SSU rRNA gene sequences of cyanobacteria (95 sequences established during this study plus 392 sequences from Nostocales and 40 sequences from non-heterocyte-forming cyanobacteria retrieved from the databases) revealed that none of the SSU rRNA gene sequences from the phyllosphere of the laurel forests was identical to a database sequence. In addition, the genetic diversity of the isolated strains was high, with 42 different genotypes (44% of the sequences) recognized. Among the new genotypes were also terrestrial members of the genus Nodularia as well as members of the genus Brasilonema. It is concluded that heterocyte-forming cyanobacteria represent a component of the phyllosphere that is still largely undersampled in subtropical/tropical forests.
Keywords: biodiversity; clonal culture; epiphyllous; heterocyte-forming cyanobacteria; rRNA sequence comparison.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Morales D., Jimenez M.S., Gonzalez-Rodríguez A.M., Cermák J. Laurel forest in Tenerife, Canary Islands. I. The site, stand structure and stand leaf area distribution. Trees. 1996;11:34–40. doi: 10.1007/s004680050055. - DOI
-
- Nogué S., De Nascimento L., Fernández-Palacios J.M., Whittaker R.J., Willis K.J. The ancient forests of La Gomera, Canary Islands, and their sensitivity to environmental change. J. Ecol. 2013;101:368–377. doi: 10.1111/1365-2745.12051. - DOI
-
- Fernández-Palacios J.M. Climatic responses of plant species on Tenerife, The Canary Islands. J. Veg. Sci. 1992;3:595–603. doi: 10.2307/3235826. - DOI
-
- Del Arco Aguilar M.J., Rodriguez Delgado O. Vegetation of the Canary Islands. In: del Arco Aguilar M.J., Rodriguez Delgado O., editors. Vegetation of the Canary Islands. Plant and Vegetation. Volume 16. Springer; Cham, Switzerland: 2018. pp. 83–319. - DOI
-
- Fernández–Palacios J.M., De Nicolás J.P. Altitudinal pattern of vegetation variation on Tenerife. J. Veg. Sci. 1995;6:183–190. doi: 10.2307/3236213. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

