Molecular Testing of Zoonotic Bacteria in Cattle, Sheep, and Goat Abortion Cases in Botswana
- PMID: 39770846
- PMCID: PMC11728289
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms12122644
Molecular Testing of Zoonotic Bacteria in Cattle, Sheep, and Goat Abortion Cases in Botswana
Abstract
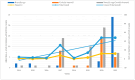
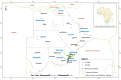
Abortion is one of the major causes of economic losses in livestock production worldwide. Because several factors can lead to abortion in cattle, sheep and goats, laboratory diagnosis, including the molecular detection of pathogens causing abortion, is often necessary. Bacterial zoonotic diseases such as brucellosis, coxiellosis, leptospirosis, and listeriosis have been implicated in livestock abortion, but they are under diagnosed and under-reported in most developing countries, including Botswana. This study applied a recently developed multiplex high-resolution melting analysis technique, coupled with singleplex qPCR assays, to investigate abortions in livestock in Botswana, using 152 samples from cattle, sheep, and goat abortion cases. Brucella spp. were the most frequent pathogen detected, with an overall frequency of 21.1%, followed by Coxiella burnetii with 19.1%. Listeria monocytogenes and Leptospira spp. were not detected in any of specimens samples investigated. Mixed infections with Brucella spp. and C. burnetii were observed in 35% specimes examined. There was a good agreement between the multiplex qPCR-HRM and singleplex qPCR for detecting Brucella spp. and C. burnetii. This study is the first report on the syndromic testing of abortion-causing pathogens in Botswana. It shows the importance of molecular methods in the differential diagnosis of abortion-causing diseases in domestic ruminants.
Keywords: brucellosis; coxiellosis; leptospirosis; listeriosis; syndromic surveillance; zoonotic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A novel multiplex qPCR‑HRM assay for the simultaneous detection of four abortive zoonotic agents in cattle, sheep, and goats.Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 28;13(1):12282. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-39447-1. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37507444 Free PMC article.
-
Occurrence of Coxiella burnetii and Chlamydiales species in abortions of domestic ruminants and in wild ruminants in Hungary, Central Europe.J Vet Diagn Invest. 2015 Mar;27(2):206-10. doi: 10.1177/1040638714563566. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2015. PMID: 25776545
-
Exposure to multiple pathogens - serological evidence for Rift Valley fever virus, Coxiella burnetii, Bluetongue virus and Brucella spp. in cattle, sheep and goat in Mali.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2022 Apr 29;16(4):e0010342. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0010342. eCollection 2022 Apr. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2022. PMID: 35486653 Free PMC article.
-
A review of coxiellosis (Q fever) and brucellosis in goats and humans: Implications for disease control in smallholder farming systems in Southeast Asia.One Health. 2023 May 22;16:100568. doi: 10.1016/j.onehlt.2023.100568. eCollection 2023 Jun. One Health. 2023. PMID: 37363211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coxiellosis in Livestock: Epidemiology, Public Health Significance, and Prevalence of Coxiella burnetii Infection in Ethiopia.Vet Med (Auckl). 2023 Aug 18;14:145-158. doi: 10.2147/VMRR.S418346. eCollection 2023. Vet Med (Auckl). 2023. PMID: 37614223 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mahabile M., Lyne M., Panin A. Factors Affecting the productivity of communal and private livestock farmers in Southern Botswana: A descriptive analysis of sample survey results. Agrekon. 2002;41:326–338. doi: 10.1080/03031853.2002.9523601. - DOI
-
- Mahabile M., Lyne M.C., Panin A. Anempirical analysis of factors affecting the productivity of livestock in Southern Botswana. Agrekon. 2005;44:99–117. doi: 10.1080/03031853.2005.9523704. - DOI
-
- Mosalagae D., Mogotsi K. Caught in a sandstorm: An assessment of pressures on communal pastoral livelihoods in the Kalahari Desert of Botswana. Pastor. Res. Policy Pract. 2013;3:18. doi: 10.1186/2041-7136-3-18. - DOI
-
- Statistics, Botswana Annual Agricultural Survey Report 2019; Traditional Sector. Gaborone, Botswana. 2019. [(accessed on 25 October 2024)]. Available online: http://www.statsbots.org.bw/
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous