Proline Improves Pullulan Biosynthesis Under High Sugar Stress Condition
- PMID: 39770859
- PMCID: PMC11728471
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms12122657
Proline Improves Pullulan Biosynthesis Under High Sugar Stress Condition
Abstract
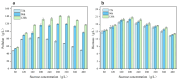
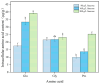
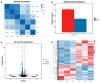
Pullulan is an extracellular polysaccharide produced via the fermentation of Aureobasidium pullulans. However, high sugar concentrations and hyperosmotic stress limit pullulan biosynthesis during the fermentation process. Therefore, we investigated the effects of proline supplementation on A. pullulans growth and pullulan biosynthesis under high sugar and hyperosmotic stress using physiological, biochemical, and transcriptomic analyses. High sugar concentrations significantly inhibited A. pullulans growth and pullulan biosynthesis. High sugar and hyperosmotic stress conditions significantly increased intracellular proline content in A. pullulans. However, treatment with proline (400 mg/L proline) significantly increased biomass and pullulan yield by 10.75% and 30.06% (174.8 g/L), respectively, compared with those in the control group. To further investigate the effect of proline on the fermentation process, we performed scanning electron microscopy and examined the activities of key fermentation enzymes. Proline treatment preserved cell integrity and upregulated the activities of key enzymes involved in pullulan biosynthesis. Transcriptome analysis revealed that most differentially expressed genes in the proline group were associated with metabolic pathways, including glycolysis/gluconeogenesis, pyruvate metabolism, and sulfur metabolism. Conclusively, proline supplementation protects A. pullulans against high sugar and hyperosmotic stress, providing a new theoretical basis and strategy for the efficient industrial production of pullulans.
Keywords: Aureobasidium pullulans; RNA sequencing; hyperglycemia; hypertonicity; proline; pullulan.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors Feng Li and Zhenxing Zhang were employed by the company Shandong Shendong Intelligent Equipment Co., Ltd. Author Qingming Zeng was employed by the company Shandong Mimei Biological Technology Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
MAL31, a sugar transporter involved in pullulan biosynthesis in Aureobasidium pullulans.J Biotechnol. 2022 Nov 20;359:176-184. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2022.10.005. Epub 2022 Oct 13. J Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36243184
-
Light calcium carbonate improves pullulan biosynthesis by Aureobasidium pullulans under high concentration of sugar.Food Chem. 2023 Jul 30;415:135760. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.135760. Epub 2023 Feb 21. Food Chem. 2023. PMID: 36854243
-
Triton X-100 improves co-production of β-1,3-D-glucan and pullulan by Aureobasidium pullulans.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Dec;104(24):10685-10696. doi: 10.1007/s00253-020-10992-3. Epub 2020 Nov 10. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 33170326
-
Taxonomy of Aureobasidium spp. and biosynthesis and regulation of their extracellular polymers.Crit Rev Microbiol. 2015 Jun;41(2):228-37. doi: 10.3109/1040841X.2013.826176. Epub 2013 Sep 9. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25168340 Review.
-
Production and applications of pullulan from lignocellulosic biomass: Challenges and perspectives.Bioresour Technol. 2023 Oct;385:129460. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2023.129460. Epub 2023 Jul 7. Bioresour Technol. 2023. PMID: 37423546 Review.
References
-
- Farris S., Unalan I.U., Introzzi L., Fuentes-Alventosa J.M., Cozzolino C.A. Pullulan-based films and coatings for food packaging: Present applications, emerging opportunities, and future challenges. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014;131:40539. doi: 10.1002/app.40539. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

