Preparation and Efficacy Evaluation of Antihyperuricemic Peptides from Marine Sources
- PMID: 39770922
- PMCID: PMC11678060
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16244301
Preparation and Efficacy Evaluation of Antihyperuricemic Peptides from Marine Sources
Abstract
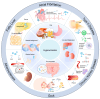
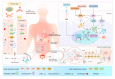
Marine-derived foods, often called blue foods, are promising sustainable alternatives to conventional food sources owing to their abundant amino acids and high protein content. Current treatments for hyperuricemia, a chronic condition attributed to purine metabolism disorders, are associated with various side effects. Novel peptide xanthine oxidase inhibitors have been discovered in the hydrolyzed products of marine fish and invertebrate proteins, which have demonstrated promising therapeutic potential by reducing uric acid levels in vitro and in vivo. This review explores the potential therapeutic effects of xanthine oxidase inhibitors derived from marine fish and invertebrates, summarizes the methods for extracting bioactive peptides from marine organisms, and emphasizes the impact of different proteases on the structure-activity relationship of bioactive peptides. The hypouricemic effects of these bioactive peptides warrant further verification. There is consensus on the in vitro chemical methods used to verify the xanthine oxidase inhibitory effects of these peptides. Considering several cell and animal model development strategies, this review summarizes several highly recognized modeling methods, proposes strategies to improve the bioavailability of bioactive peptides, and advocates for a diversified evaluation system. Although the screening and evaluation methods for antihyperuricemic peptides have been shown to be feasible across numerous studies, they are not optimal. This review examines the deficiencies in bioavailability, synthesis efficiency, and evaluation mechanisms in terms of their future development and proposes potential solutions to address these issues. This review provides a novel perspective for the exploration and application of marine-derived hypouricemic bioactive peptides.
Keywords: hyperuricemia; marine bioactive peptides; uric acid; xanthine oxidase.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Wenmei Huang was employed by the company Xiamen Daozhiyuan Biological Technology Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Rathinam R.B., Acharya A., Robina A.J., Banu H., Tripathi G. The immune system of marine invertebrates: Earliest adaptation of animals. Comp. Immunol. Rep. 2024;7:200163. doi: 10.1016/j.cirep.2024.200163. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2024R1047/the Basic Research Program for Provincial Public Welfare Research Institutes in Fujian Provinceand [grant number
- FJHYF-L-2023-23/the Special Funds Program for Promoting High-Quality Development of Marine and Fishery Industry in Fujian Province
- 2021FJSCZY02/the Innovation and Industrialization Development of Abalone Seed Industry
- FJHY-YYKJ-2024-1-3/the Special Fund Project for High-Quality Development of Marine Services and Fisheries in Fujian Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources