The Impact and Efficacy of Vitamin D Fortification
- PMID: 39770943
- PMCID: PMC11677708
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16244322
The Impact and Efficacy of Vitamin D Fortification
Abstract
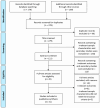
Vitamin D deficiency is a global health issue linked to various chronic diseases and overall mortality. It primarily arises from insufficient sunlight exposure, compounded by dietary limitations. Vitamin D fortification of commonly consumed foods has emerged as a viable public health intervention to address this deficiency. This review evaluates the impact of vitamin D food fortification on serum levels, intake, and health outcomes and explores the stability, bio-accessibility, bioavailability, and cost-effectiveness of such interventions. A comprehensive literature search was conducted in PubMed and Google Scholar, focusing on studies from 2015 to 2024. The criteria included primary research on healthy adults that addressed the effects of vitamin D fortification on health, intake, and serum levels, as well as the fortification's stability, bio-accessibility, bioavailability, and cost-effectiveness. Studies were extracted and analyzed according to PRISMA guidelines. The review included 31 studies from diverse geographic locations, revealing that fortifying dairy products, cereals, fats, oils, and other food items effectively increased serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels. The fortification methods varied, with vitamin D3 showing superior efficacy over vitamin D2. Encapsulation techniques improved stability and bioavailability. Fortifying staple foods like milk and eggs proved cost-effective compared with pharmaceutical interventions. Vitamin D food fortification significantly enhances serum levels and intake, with dairy and cereals being the most frequently fortified. Standardized fortification guidelines are essential to ensure safety and efficacy. Ongoing evaluation and region-specific policies are crucial for effectively optimizing fortification strategies and addressing vitamin D deficiency.
Keywords: bio-accessibility; bioavailability; cost-effectiveness; food fortification; fortification doses; fortification methods; stability; vitamin D.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
-
- da Silva A.B.J., Barros W.M.A., da Silva M.L., Silva J.M.L., da Silva Souza A.P., da Silva K.G., de Sousa Fernandes M.S., da Fonseca Carneiro A.C.B., de Oliveira Nogueira Souza V., Lagranha C.J. Impact of vitamin D on cognitive functions in healthy individuals: A systematic review in randomized controlled clinical trials. Front. Psychol. 2022;13:987203. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.987203. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sohouli M.H., Wang S., Almuqayyid F., Gabiatti M.P., Mozaffari F., Mohamadian Z., Koushki N., Alras K.A., AlHossan A.M., Albatati S.K., et al. Impact of vitamin D supplementation on markers of bone turnover: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2023;14:1150187. doi: 10.1111/eci.14038. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical