Impact of Omega-3 on Endocannabinoid System Expression and Function, Enhancing Cognition and Behavior in Male Mice
- PMID: 39770965
- PMCID: PMC11676180
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16244344
Impact of Omega-3 on Endocannabinoid System Expression and Function, Enhancing Cognition and Behavior in Male Mice
Abstract
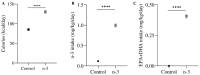
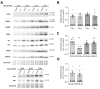
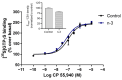
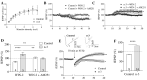
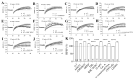
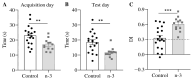
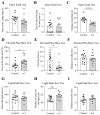
Background/Objectives: Omega-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) support brain cell membrane integrity and help mitigate synaptic plasticity deficits. The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is integral to synaptic plasticity and regulates various brain functions. While PUFAs influence the ECS, the effects of omega-3 on the ECS, cognition, and behavior in a healthy brain remain unclear. Methods and Results: Here, we demonstrate that hippocampal synaptosomes from male mice fed an omega-3-rich diet exhibit increased levels of cannabinoid CB1 receptors (~30%), phospholipase C β1 (PLCβ1, ~30%), monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL, ~30%), and cannabinoid receptor-interacting protein 1a (Crip1a, ~60%). Conversely, these synaptosomes show decreased levels of diacylglycerol lipase α (DAGLα, ~40%), synaptosomal-associated protein 25kDa (SNAP-25, ~30%), and postsynaptic density protein 95 (PSD-95, ~40%). Omega-3 intake also reduces Gαo and Gαi3 levels, though receptor-stimulated [35S]GTPγS binding remains unaffected. Stimulation of the medial perforant path (MPP) induced long-term potentiation (LTP) in omega-3-fed mice. This LTP was dependent on group I metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR), 2 arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), CB1 receptors, N-type Ca2+ channels, and actin filaments. Behaviorally, omega-3-fed mice displayed reduced exploratory behavior and significantly improved object discrimination in the novel object recognition test (NORT). They also spent more time in open arms and exhibited reduced freezing time in the elevated plus maze (EPM), indicative of reduced anxiety-like behavior. Conclusions: Our findings suggest that omega-3 leverages the ECS to enhance brain function under normal conditions.
Keywords: CB1 receptor; hippocampus; memory; polyunsaturated fatty acids; synaptic plasticity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Aguilera García C., Navarro Alarcón M., Alonso Aperte E., Alvarez Mercado A.I., Andrés Carvajales P., Arredondo Olguín M. Tratado de Nutrición. Tomo I. Bases Fisiológicas y Bioquímicas de la Nutrición. Médica Panamericana; Madrid, Spain: 2010. 963p
-
- Gómez Candela C., Bermejo López L.M., Loria Kohen V. Importance of a balanced omega 6/omega 3 ratio for the maintenance of health. Nutritional recommendations. Nutr. Hosp. 2011;26:323–329. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

