Folic Acid Prevents High-Fat Diet-Induced Postpartum Weight Retention in Rats, Which Is Associated with a Reduction in Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Mediated Hepatic Lipogenesis
- PMID: 39770997
- PMCID: PMC11676124
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16244377
Folic Acid Prevents High-Fat Diet-Induced Postpartum Weight Retention in Rats, Which Is Associated with a Reduction in Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Mediated Hepatic Lipogenesis
Abstract
Background: Proactively preventing postpartum weight retention (PPWR) is one of the effective intervention strategies to reduce the occurrence of obesity in women. Population studies have shown that serum folate levels are closely related to body weight. The regulation of folic acid on lipid metabolism has been fully confirmed in both in vivo and in vitro studies. For many years, folic acid supplementation has been widely used in periconceptional women due to its role in preventing fetal neural tube defects. However, whether folic acid supplementation prior to and throughout pregnancy exerts preventive effects on PPWR remains uncertain. This study aims to investigate the preventive effect of folic acid on PPWR in rats and further explore the underlying mechanisms.
Methods: In this study, pregnant rats were administered one of the dietary schedules: control diet (CON), high-fat diet (HF), control diet combined with folic acid (FA) and high-fat diet combined with folic acid (HF + FA).
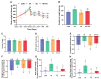
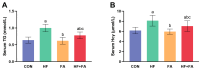
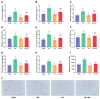
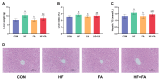
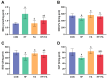
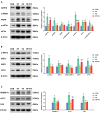
Results: We discovered that folic acid supplementation inhibited high-fat diet-induced elevations in body weight, visceral fat weight, liver weight, hepatic lipid levels and serum lipid levels at 1 week post-weaning (PW). Western blot analysis showed that folic acid supplementation inhibited the expression of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-specific proteins including GRP78, PERK, eIF2α, IRE1α, XBP1 and ATF6, subsequently decreasing the expression of proteins related to lipid synthesis including SREBP-1c, ACC1 and FAS.
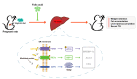
Conclusions: In conclusion, folic acid supplementation prior to and throughout pregnancy exerts preventive effects on high-fat diet-induced PPWR in rats, and the mechanism is associated with the inhibition of ER stress-mediated lipogenesis signaling pathways in the liver. Folic acid supplementation may serve as a potential strategy for preventing PPWR. In the future, the effectiveness of folic acid in PPWR prevention can be further verified by population studies.
Keywords: endoplasmic reticulum stress; folic acid; postpartum weight retention.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
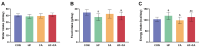
Similar articles
-
Fagopyrum dibotrys extract improves nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via inhibition of lipogenesis and endoplasmic reticulum stress in high-fat diet-fed mice.BMC Res Notes. 2024 Oct 16;17(1):310. doi: 10.1186/s13104-024-06962-x. BMC Res Notes. 2024. PMID: 39415220 Free PMC article.
-
Folic acid intervention ameliorates hepatic steatosis after long-term alcohol exposure by alleviating endoplasmic reticulum stress.J Nutr Biochem. 2025 Jul;141:109896. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2025.109896. Epub 2025 Mar 6. J Nutr Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40054675
-
Caveolin 1 in bovine liver is associated with fatty acid-induced lipid accumulation and the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response: Role in fatty liver development.J Dairy Sci. 2025 Jan;108(1):1007-1021. doi: 10.3168/jds.2024-25349. Epub 2024 Sep 28. J Dairy Sci. 2025. PMID: 39343220
-
Preventive Effect of Apple Polyphenol Extract on High-Fat Diet-Induced Hepatic Steatosis in Mice through Alleviating Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress.J Agric Food Chem. 2022 Mar 16;70(10):3172-3180. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c07733. Epub 2022 Mar 1. J Agric Food Chem. 2022. PMID: 35227062
-
Effects of oral selenium and magnesium co-supplementation on lipid metabolism, antioxidative status, histopathological lesions, and related gene expression in rats fed a high-fat diet.Lipids Health Dis. 2018 Jul 21;17(1):165. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0815-4. Lipids Health Dis. 2018. PMID: 30031400 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang J., Yang Z.Y., Pang X.H., Duan Y.F., Jiang S., Zhao L.Y., Yin S.A., Lai J.Q. The status of postpartum weight retention and its associated factors among Chinese lactating women in 2013. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi [Chin. J. Prev. Med.] 2016;50:1067–1073. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

