Acute Co-Ingestion of Caffeine and Sodium Bicarbonate on Muscular Endurance Performance
- PMID: 39771003
- PMCID: PMC11677328
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16244382
Acute Co-Ingestion of Caffeine and Sodium Bicarbonate on Muscular Endurance Performance
Abstract
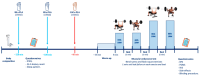
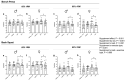
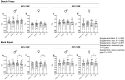
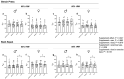
Background: Caffeine and sodium bicarbonate individually enhance muscular endurance by delaying fatigue, but their combined effects have scarcely been studied. Objectives: This study aimed to evaluate the acute effects of co-ingesting caffeine and sodium bicarbonate on muscular endurance at different loads in bench press and back squat exercises. Methods: Twenty-seven recreationally trained participants (female/male: 14/14; age: 23 ± 3.6 years) were randomized to four conditions in a double-blind, crossover design: (a) sodium bicarbonate and caffeine (NaHCO3 + CAF); (b) sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3); (c) caffeine (CAF); (d) placebo (PLA); ingesting 0.3 g/kg NaHCO3, 3 mg/kg caffeine or placebo (maltodextrin). Participants performed two muscle endurance tests on bench press and back squat exercises at 65% and 85% 1RM, performing as many repetitions as possible in one set until task failure. Results: CAF increased the number of repetitions (p < 0.001; ηp2 = 0.111), mean velocity (Vmean, p = 0.043, ηp2 = 0.16), and mean power output (Wmean, p = 0.034, ηp2 = 0.15) compared to placebo. These effects were observed in back squat exercise at 65%1RM in Vmean (3.7%, p = 0.050, g = 1.144) and Wmean (5.2%, p = 0.047, g = 0.986) and at 85%1RM in Vmean (5.4%, p = 0.043, g = 0.22) and Wmean (5.5%, p = 0.050, g = 0.25). No ergogenic effects were found in NaHCO3 + CAF) or NaHCO3 conditions. Conclusions: CAF increased muscular endurance performance in male and female participants by increasing the number of repetitions, mean velocity, and power output; however, when NaHCO3 was ingested, these effects were not detected.
Keywords: caffeine; ergogenic aids; load-power relationship; resistance exercise; sodium bicarbonate; sport nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Grgic J., Pedisic Z., Saunders B., Artioli G.G., Schoenfeld B.J., McKenna M.J., Bishop D.J., Kreider R.B., Stout J.R., Kalman D.S., et al. International Society of Sports Nutrition position stand: Sodium bicarbonate and exercise performance. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2021;18:61. doi: 10.1186/s12970-021-00458-w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Guest N.S., VanDusseldorp T.A., Nelson M.T., Grgic J., Schoenfeld B.J., Jenkins N.D.M., Arent S.M., Antonio J., Stout J.R., Trexler E.T., et al. International society of sports nutrition position stand: Caffeine and exercise performance. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2021;18:1. doi: 10.1186/s12970-020-00383-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

