Investigation into the Potential Mechanism of Radix Paeoniae Rubra Against Ischemic Stroke Based on Network Pharmacology
- PMID: 39771032
- PMCID: PMC11678013
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16244409
Investigation into the Potential Mechanism of Radix Paeoniae Rubra Against Ischemic Stroke Based on Network Pharmacology
Abstract
Background: Radix Paeoniae Rubra (RPR), an edible and medicinal Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), is extensively employed in therapeutic interventions of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. However, the curative effect of RPR on ischemic stroke remains ambiguous. This work integrated network pharmacology, molecular docking, and experimental validation to explore the mechanisms of RPR in treating ischemic stroke.
Methods: In this study, we preliminarily elucidated the therapeutic effect and mechanism of RPR on ischemic stroke through network pharmacology, molecular docking analysis, and experimental verification.
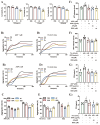
Results: The results indicated that RPR improved the neurological deficit scores, decreased the size of infarcts, and reduced brain edema symptoms in the tMCAO mice model. Furthermore, through network pharmacology and molecular docking, four core targets (MAPK3, TNF-α, MAPK14, and JNK) closely related to RPR's treatment of ischemic stroke were identified, exhibiting strong affinity with two key active components of RPR: albiflorin (AF) and β-sitosterol (BSS). The Western blot showed the potential mechanism of RPR treatment for ischemic stroke by regulating the MAPK signaling pathway. Moreover, RPR and its main active ingredients exhibited a significant inhibitory effect on platelets.
Conclusion: In conclusion, this study revealed that RPR alleviates ischemic injury by activating the MAPK signaling pathway, and its protective effect may partly stem from inhibiting platelet activation. This work may provide a scientific basis for the development and utilization of RPR as a natural edible material to prevent ischemic stroke and anti-platelet therapy.
Keywords: Radix Paeoniae Rubra; albiflorin; ischemic stroke; platelet; β-sitosterol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures








References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HXYS19001, HXYS19002/Innovative Chinese Medicine and Health Products Research Academician Workstation of Academician Boli Zhang and Academician Beiwei Zhu, West China Hospital, Sichuan University
- ZYXY21002/the 1⋅3⋅5 Project for Disciplines 456 of Excellence, West China Hospital, Sichuan University
- No. 161200012/Innovative Chinese Medicine Preclinical Research Fund of "Liqing 457 No. 2", West China Hospital, Sichuan University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

