Accumulation of Microplastics and Potentially Toxic Elements in Plant Leaves Along an Urbanization Gradient in Bangladesh
- PMID: 39771063
- PMCID: PMC11679090
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics12120848
Accumulation of Microplastics and Potentially Toxic Elements in Plant Leaves Along an Urbanization Gradient in Bangladesh
Abstract
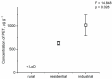
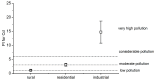
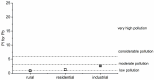
Potentially toxic elements (PTEs) and microplastics (MPs) in the atmosphere raise widespread apprehension due to their association with the ecosystem and public health. The accumulation of airborne MPs and PTEs was analyzed in Polyalthia longifolia leaves, and the Pollution Index (PI) was calculated along an industrial, residential, and rural gradient in Bangladesh. Only polyethylene terephthalate (PET) was found in the highest concentration in industrial areas compared to other areas. In leaves, a significantly higher Cd, Pb, and Zn concentration was found in industrial regions compared to residential and rural areas. For Cd, the PI was observed to be higher than 1 in rural areas, indicating a moderate level of pollution; it was higher than 3 in residential areas, showing considerable pollution; and it was found to be more than 6 in industrial areas. The higher concentration of both MPs and PTEs with increasing urbanization reflects the influence of anthropogenic activities. The findings of the study demonstrate the fascinating potential of P. longifolia tree leaves as a promising bioindicator for air quality biomonitoring.
Keywords: air pollution; bioindicator; leaf dust; microplastics; pollution index.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Karacocuk T., Sevik H., Isinkaralar K., Turkyilmaz A., Cetin M. The Change of Cr and Mn Concentrations in Selected Plants in Samsun City Center Depending on Traffic Density. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2022;18:75–83. doi: 10.1007/s11355-021-00483-6. - DOI
-
- Cetin M., Jawed A.A. Variation of Ba Concentrations in Some Plants Grown in Pakistan Depending on Traffic Density. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2022;14:3785–3791. doi: 10.1007/s13399-022-02334-2. - DOI
-
- Serbula S.M., Kalinovic T.S., Ilic A.A., Kalinovic J.V., Steharnik M.M. Assessment of Airborne Heavy Metal Pollution Using Pinus spp. and Tilia spp. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2013;13:563–573. doi: 10.4209/aaqr.2012.06.0153. - DOI
-
- Yadav S., Rajamani V. Air Quality and Trace Metal Chemistry of Different Size Fractions of Aerosols in N–NW India—Implications for Source Diversity. Atmos. Environ. 2006;40:698–712. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2005.10.005. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

