Effects of Far-Red Light and Ultraviolet Light-A on Growth, Photosynthesis, Transcriptome, and Metabolome of Mint (Mentha haplocalyx Briq.)
- PMID: 39771193
- PMCID: PMC11728695
- DOI: 10.3390/plants13243495
Effects of Far-Red Light and Ultraviolet Light-A on Growth, Photosynthesis, Transcriptome, and Metabolome of Mint (Mentha haplocalyx Briq.)
Abstract
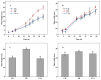
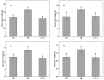
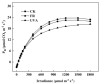
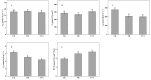
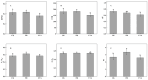
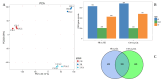
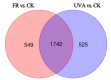
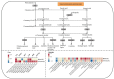
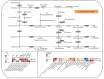
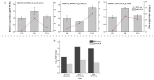
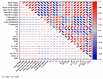
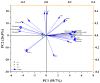
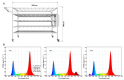
To investigate the effects of different light qualities on the growth, photosynthesis, transcriptome, and metabolome of mint, three treatments were designed: (1) 7R3B (70% red light and 30% blue light, CK); (2) 7R3B+ far-red light (FR); (3) 7R3B+ ultraviolet light A (UVA). The results showed that supplemental FR significantly promoted the growth and photosynthesis of mint, as evidenced by the increase in plant height, plant width, biomass, effective quantum yield of PSII photochemistry (Fv'/Fm'), maximal quantum yield of PSII (Fv/Fm), and performance index (PI). UVA and CK exhibited minimal differences. Transcriptomic and metabolomic analysis indicated that a total of 788 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and 2291 differential accumulated metabolites (DAMs) were identified under FR treatment, mainly related to plant hormone signal transduction, phenylpropanoid biosynthesis, and flavonoid biosynthesis. FR also promoted the accumulation of phenylalanine, sinapyl alcohol, methylchavicol, and anethole in the phenylpropanoid biosynthesis pathway, and increased the levels of luteolin and leucocyanidin in the flavonoid biosynthesis pathway, which may perhaps be applied in practical production to promote the natural antibacterial and antioxidant properties of mint. An appropriate increase in FR radiation might alter transcript reprogramming and redirect metabolic flux in mint, subsequently regulating its growth and secondary metabolism. Our study uncovered the regulation of FR and UVA treatments on mint in terms of growth, physiology, transcriptome, and metabolome, providing reference for the cultivation of mint and other horticultural plants.
Keywords: far-red radiation; flavonoid; metabolome; mint; phenylpropanoid; transcriptome; ultraviolet-a.
Conflict of interest statement
The author Lijun Bu was employed by the company “Shanghai Sunqiaoyijia Tech-Agriculture Co., Ltd.”. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Bian Z.H., Cheng R.F., Wang Y., Yang Q.C., Lu C.G. Effect of green light on nitrate reduction and edible quality of hydroponically grown lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) under short-term continuous light from red and blue light-emitting diodes. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2018;153:63–71. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2018.05.010. - DOI
-
- Li Y.F., Xin G.F., Wei M., Shi Q.H., Yang F.J., Wang X.F. Carbohydrate accumulation and sucrose metabolism responses in tomato seedling leaves when subjected to different light qualities. Sci. Hortic. 2017;225:490–497. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2017.07.053. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

