Genetic Transformation of Torenia fournieri L. with the Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ab Gene Confers Resistance to Mythimna separata (Walker)
- PMID: 39771266
- PMCID: PMC11678925
- DOI: 10.3390/plants13243568
Genetic Transformation of Torenia fournieri L. with the Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ab Gene Confers Resistance to Mythimna separata (Walker)
Abstract
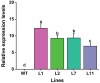
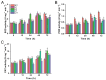
Torenia fournieri L. is a popular ornamental plant in the genus Torenia, widely used in commercial landscaping, especially during the summer. Additionally, Torenia has served as a model ornamental plant in many studies exploring ornamental characteristics and pest control through genetic engineering. To date, no research has been reported on developing insect-resistant Torenia expressing genes from Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt). In this study, a recombinant vector carrying the Cry1Ab gene from Bt, pBI121-Cry1Ab, was constructed and transferred into T. fournieri via Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation. A total of 13 shoots survived on the kanamycin selection medium, among which four putative transgenic lines, designated L1, L2, L7, and L11, were molecularly confirmed by PCR and Southern blot analysis, indicating successful integration of the Cry1Ab gene into the genomes of these lines. Quantitative real-time PCR and ELISA results further verified the successful expression of the Cry1Ab gene in the leaves of all four transgenic lines. Insect bioassay results demonstrated that all four transgenic lines showed strong resistance to the insect pest, Mythimna separata, with mortality rates ranging from 59.9% to 100.0%, in contrast to a larval mortality rate of 16.2% in the wild-type Torenia. Additionally, these transgenic lines significantly decreased in larval survival rates compared to those fed on wild-type plants. Furthermore, these transgenic lines activated superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity at 12 and 24 h, and catalase (CAT) activity at 72 h, while suppressing SOD activity at 72 h, and peroxidase (POD) activity over time. Our findings indicate that these transgenic lines exhibit high resistance to the insect pest and provide new insights into controlling insect pests in ornamental plants through genetic approaches.
Keywords: Cry1Ab; insect resistance; oriental armyworm; protective enzymes; transgenic Torenia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

