Phytochemical and Cytotoxic Aspects of Amaryllidaceae Alkaloids in Galanthus Species: A Review
- PMID: 39771275
- PMCID: PMC11678157
- DOI: 10.3390/plants13243577
Phytochemical and Cytotoxic Aspects of Amaryllidaceae Alkaloids in Galanthus Species: A Review
Abstract
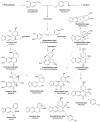
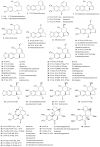
The genus Galanthus (Amaryllidaceae) currently contains 25 plant species naturally occurring in Europe and the Middle East region. These perennial bulbous plants possess well-known medicinal and ornamental qualities. Alkaloid diversity is their most distinctive phytochemical feature. A total of 127 compounds (≈20% of all known Amaryllidaceae alkaloids) grouped in 16 structural types have been previously found in Galanthus extracts. Some structural types like galanthindole, graciline and plicamine were first discovered in Galanthus plants. Nine Galanthus species, however, remain unstudied regarding their alkaloid patterns. Intraspecific variability has only been studied in G. nivalis and G. elwesii. Amaryllidaceae alkaloids are molecules with anticholinesterase, antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral and anticancer properties. Galanthamine, isolated for the first time from Galanthus woronowii Losinsk., stands out as an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor approved for medical use by the FDA for the treatment of symptoms of Alzheimer's disease. Lycorine, narciclasine and pancratistatin are noteworthy cytotoxic and antitumor alkaloids. Structural types like galanthamine, homolycorine and haemanthamine are fairly well studied in anticancer research, but little to no information is available on galanthindole, graciline and other types. This review aims to present an update on the alkaloid diversity of Galanthus spp. and highlight the need for further research on the antitumor potential of these molecules.
Keywords: Amaryllidaceae alkaloids; Galanthus; anticancer; biological activities; cytotoxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Alkaloid diversity in Galanthus elwesii and Galanthus nivalis.Chem Biodivers. 2011 Jan;8(1):115-30. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.200900380. Chem Biodivers. 2011. PMID: 21259423
-
Therapeutic and medicinal effects of snowdrop (Galanthus spp.) in Alzheimer's disease: A review.J Educ Health Promot. 2023 Apr 28;12:128. doi: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_451_22. eCollection 2023. J Educ Health Promot. 2023. PMID: 37397105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intraspecific variability in the alkaloid metabolism of Galanthus elwesii.Phytochemistry. 2004 Mar;65(5):579-86. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2003.12.013. Phytochemistry. 2004. PMID: 15003421
-
Towards a molecular understanding of the biosynthesis of amaryllidaceae alkaloids in support of their expanding medical use.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 May 31;14(6):11713-41. doi: 10.3390/ijms140611713. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23727937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological Activities of Snowdrop (Galanthus spp., Family Amaryllidaceae).Front Pharmacol. 2021 Feb 19;11:552453. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.552453. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33679383 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Occurrence and Bioactivities of Amaryllidaceae Alkaloids from Plants: A Taxonomy-Guided Genera-Wide Review.Plants (Basel). 2025 Jun 24;14(13):1935. doi: 10.3390/plants14131935. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40647943 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Plants of the World Online. [(accessed on 16 December 2024)]. Available online: https://powo.science.kew.org/
-
- Davis A.P. The genus Galanthus. In: Mathew B., editor. A Botanical Magazine Monograph. Timber Press Inc.; Portland, OR, USA: 1999. pp. 15–17, 48–51.
-
- IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. [(accessed on 11 November 2024)]. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/
-
- Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora, Export Quotas. [(accessed on 4 October 2024)]. Available online: https://cites.org/eng/resources/quotas/export_quotas.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

