Ultrasonic Effect on the Growth of Crystals from Aqueous Electrolyte Solutions on Polymer Substrates: The Role of Isotopic Composition of Liquid
- PMID: 39771430
- PMCID: PMC11679036
- DOI: 10.3390/polym16243580
Ultrasonic Effect on the Growth of Crystals from Aqueous Electrolyte Solutions on Polymer Substrates: The Role of Isotopic Composition of Liquid
Abstract
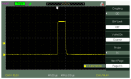
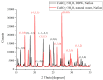
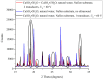
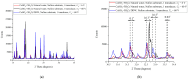
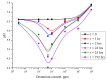
The peculiarities of the crystal formation from supersaturated aqueous solutions of CuSO4 on polymer substrates were studied using X-ray diffractometry. During the crystal formation, the test solutions were irradiated with one or two counter-propagating ultrasonic beams. Test solutions were prepared using natural deionized water with a deuterium content of 157 ± 1 ppm. The other liquid used was deuterium-depleted water with a deuterium content of 3 ppm. It was shown that irradiation with one/two ultrasonic beams resulted in drastic changes in the structure of the crystal deposit formed on the polymer substrate in the case when natural deionized water was chosen for preparing the supersaturated solution of CuSO4.
Keywords: X-ray diffractometry; aqueous electrolyte solution; crystallization; deionized water; polymer membrane; ultrasonic beam.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nafion: A Flexible Template for Selective Structuring.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Mar 8;16(6):744. doi: 10.3390/polym16060744. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38543350 Free PMC article.
-
Possibility to Alter Dynamics of Luminescence from Surface of Polymer Membrane with Ultrasonic Waves.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Jun 22;14(13):2542. doi: 10.3390/polym14132542. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35808587 Free PMC article.
-
Adsorption of Methylene Blue on the Surface of Polymer Membrane; Dependence on the Isotopic Composition of Liquid Matrix.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Sep 25;14(19):4007. doi: 10.3390/polym14194007. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36235955 Free PMC article.
-
Nafion: New and Old Insights into Structure and Function.Polymers (Basel). 2023 May 7;15(9):2214. doi: 10.3390/polym15092214. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37177360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nucleation of solid solutions crystallizing from aqueous solutions.Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2003 Mar 15;361(1804):615-31; discussion 632. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2002.1142. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2003. PMID: 12662457 Review.
References
-
- Geddert T., Augustin W., Scholl S. Induction Time in Crystallization Fouling on Heat Transfer Surfaces. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2011;34:1303–1310. doi: 10.1002/ceat.201000469. - DOI
-
- Herz A., Malayeri M., Müller-Steinhagen H. Fouling of roughened stainless steel surfaces during convective heat transfer to aqueous solutions. Energy Convers. Manag. 2008;49:3381–3386. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2007.09.034. - DOI
-
- Bogacz W., Lemanowicz M., Al-Rashed M.H., Nakonieczny D., Piotrowski T., Wójcik J. Impact of roughness, wettability and hydrodynamic conditions on the incrustation on stainless steel surfaces. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017;112:352–361. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2016.10.076. - DOI
-
- Gao Z., Rohani S., Gong J., Wang J. Recent Developments in the Crystallization Process: Toward the Pharmaceutical Industry. Engineering. 2017;3:343–353. doi: 10.1016/J.ENG.2017.03.022. - DOI
-
- Bałdyga J., Tyl G., Bouaifi M. Application of Gaussian cubature to model two-dimensional population balances. Chem. Process. Eng. 2017;38:393–409. doi: 10.1515/cpe-2017-0030. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

