Participation of Polymer Materials in the Structure of Piezoelectric Composites
- PMID: 39771453
- PMCID: PMC11678843
- DOI: 10.3390/polym16243603
Participation of Polymer Materials in the Structure of Piezoelectric Composites
Abstract
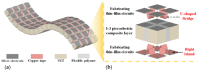
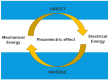
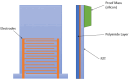
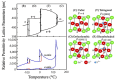
This review explores the integration of polymer materials into piezoelectric composite structures, focusing on their application in sensor technologies, and wearable electronics. Piezoelectric composites combining ceramic phases like BaTiO3, KNN, or PZT with polymers such as PVDF exhibit significant potential due to their enhanced flexibility, processability, and electrical performance. The synergy between the high piezoelectric sensitivity of ceramics and the mechanical flexibility of polymers enables the development of advanced materials for biomedical devices, energy conversion, and smart infrastructure applications. This review discusses the evolution of lead-free ceramics, the challenges in improving polymer-ceramic interfaces, and innovations like 3D printing and surface functionalization, which enhance charge transfer and material durability. It also covers the effects of radiation on these materials, particularly in nuclear applications, and strategies to enhance radiation resistance. The review concludes that polymer materials play a critical role in advancing piezoelectric composite technologies by addressing environmental and functional challenges, paving the way for future innovations.
Keywords: lead-free ceramics; piezoelectric; polymers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

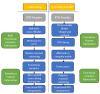
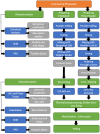
References
-
- Newnham R.E., Skinner D.P., Cross L.E. Composite Piezoelectric Transducers. Mater. Des. 1980;2:93–106. doi: 10.1016/0261-3069(80)90019-9. - DOI
-
- Arnau A., Soares D. Piezoelectric Transducers and Applications. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2008. Fundamentals of Piezoelectricity.
-
- Holterman J., Groen P. An Introduction to Piezoelectric Materials and Components. Stichting Applied Piezo; Apeldoorn, The Netherlands: 2012.
-
- Yuan C., Zhang C., Yang C., Wu F., Xiao S., Sun H. Enhanced Piezoelectric Properties of Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride)/Lead Zirconate Titanate (PVDF/PZT) Fiber Films Fabricated by Electrospinning. J. Electron. Mater. 2023;52:7193–7207. doi: 10.1007/s11664-023-10631-3. - DOI
-
- Habib M., Lantgios I., Hornbostel K. A review of ceramic, polymer and composite piezoelectric materials. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2022;55:423002. doi: 10.1088/1361-6463/ac8687. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

