Formulation and Characterization of β-Cyclodextrins-Nitazoxanide Inclusion Complexes: Enhanced Solubility, In Vitro Drug Release, and Antiviral Activity in Vero Cells
- PMID: 39771475
- PMCID: PMC11677481
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16121494
Formulation and Characterization of β-Cyclodextrins-Nitazoxanide Inclusion Complexes: Enhanced Solubility, In Vitro Drug Release, and Antiviral Activity in Vero Cells
Abstract
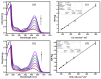
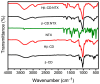
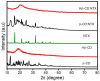
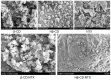
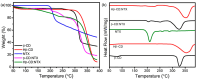
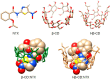
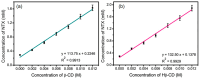
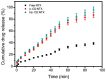
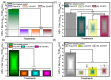
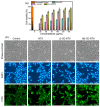
Background/Objectives: Nitazoxanide (NTX) exhibits promising therapeutic potential; its effectiveness is constrained by its low oral bioavailability due to its poor water solubility and limited permeability. Methods: This study focused on developing a complex of NTX with β-cyclodextrins (β-CDs), specifically β-CD and hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (Hβ-CD), to enhance the solubility and antiviral activity of NTX. Results: The formation of the β-CD:NTX in an aqueous solution was verified using UV-visible spectroscopy, confirming a 1:1 inclusion complex. Characterization of the solid β-CD:NTX complexes was confirmed via FTIR, X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and DSC-TGA analyses. Molecular docking studies revealed that the NTX thiazole ring with the nitro group was positioned within the β-CDs cavity, while the benzene ring remained outside. Phase solubility tests showed that β-CD:NTX complexes were formed with high stability constants, demonstrating a linear increase in NTX solubility as the β-CD concentration increased. Dissolution tests revealed rapid and nearly complete NTX release within 90 min for β-CD:NTX and Hβ-CD:NTX complexes. The β-CD:NTX complexes were tested for their antiviral activity against Herpes simplex virus (HSV-1) cultures. Results showed that the Hβ-CD:NTX complex had significantly higher antiviral efficacy than β-CD:NTX and free NTX alone. Moreover, cytotoxicity and cellular uptake studies on Vero cells indicated that the Hβ-CD:NTX complex demonstrated lower cytotoxicity and had the highest IC50 value, followed by β-CD:NTX and free NTX. Conclusions: These findings suggest that Hβ-CD:NTX inclusion complexes may serve as effective carriers for delivering NTX in HSV-1 treatments using Vero cell models.
Keywords: antiviral activity; in vitro drug release; inclusion complexes; nitazoxanide; solubility; β-cyclodextrins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

