Hydroxytyrosol: A Promising Therapeutic Agent for Mitigating Inflammation and Apoptosis
- PMID: 39771483
- PMCID: PMC11728517
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16121504
Hydroxytyrosol: A Promising Therapeutic Agent for Mitigating Inflammation and Apoptosis
Abstract
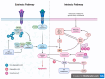
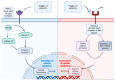
Inflammation and apoptosis are interrelated biological processes that have a significant impact on the advancement and growth of certain chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular problems, neurological conditions, and osteoarthritis. Recent research has emphasized that focusing on these mechanisms could result in novel therapeutic approaches that aim to decrease the severity of diseases and enhance patient outcomes. Hydroxytyrosol (HT), which is well-known for its ability to prevent oxidation, has been identified as a possible candidate for regulating both inflammation and apoptosis. In this review, we will highlight the multifaceted benefits of HT as a therapeutic agent in mitigating inflammation, apoptosis, and associated conditions. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the latest in vitro and in vivo research on the anti-inflammatory and antiapoptotic effects of HT and the mechanisms by which it works. Based on these studies, it is strongly advised to use HT as a bioactive ingredient in pharmaceutical products intended for mitigating inflammation, as well as those with apoptosis applications.
Keywords: apoptosis; hydroxytyrosol; inflammation; natural products.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

