Preparation and In Vitro/In Vivo Characterization of Mixed-Micelles-Loaded Dissolving Microneedles for Sustained Release of Indomethacin
- PMID: 39771485
- PMCID: PMC11728531
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16121505
Preparation and In Vitro/In Vivo Characterization of Mixed-Micelles-Loaded Dissolving Microneedles for Sustained Release of Indomethacin
Abstract
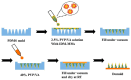
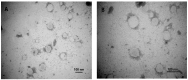
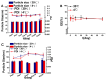
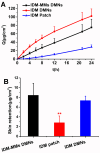
Background/Objectives: Indomethacin (IDM) is commonly used to treat chronic inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. However, long-term oral IDM treatment can harm the gastrointestinal tract. This study presents a design for encapsulating IDM within mixed micelles (MMs)-loaded dissolving microneedles (DMNs) to improve and sustain transdermal drug delivery. Methods: Indomethacin-loaded mixed micelles (IDM-MMs) were prepared from Soluplus® and Poloxamer F127 by means of a thin-film hydration method. The MMs-loaded DMNs were fabricated using a two-step molding method and evaluated for storage stability, insertion ability, in vitro release, in vitro transdermal penetration, and in vivo PK/PD studies. Results: The obtained MMs were stable at 4 °C and 30 °C for 60 days. The in vitro IDM transdermal penetration was remarkably improved by the MMs-loaded DMNs compared to a commercial patch. A pharmacokinetic study demonstrated that the MMs-loaded DMNs had a relative bioavailability of 4.1 in comparison with the commercial patch. Furthermore, the MMs-loaded DMNs showed a significantly shorter lag time than the commercial patch, as well as a more stable plasma concentration than the DMNs without MMs. The therapeutic efficacy of the IDM DMNs was examined in Complete Freund's Adjuvant-induced arthritis mice. The IDM DMN treatment effectively reduced arthritis severity, resulting in decreased paw swelling, arthritis index, spleen hyperplasia, and serum IL-1β and TNF-α levels. Conclusions: Our findings demonstrated that the novel MMs-loaded DMNs were an effective strategy for sustained IDM release, providing an alternate route of anti-inflammatory drug delivery.
Keywords: adjuvant induced arthritis; dissolving microneedles; indomethacin; mixed micelles; sustained release.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of this article.
Figures







References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

