Innovative Approaches to Enhancing the Biomedical Properties of Liposomes
- PMID: 39771504
- PMCID: PMC11728823
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16121525
Innovative Approaches to Enhancing the Biomedical Properties of Liposomes
Abstract
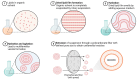
Liposomes represent a promising class of drug delivery systems that enhance the therapeutic efficacy and safety of various pharmaceutical agents. Also, they offer numerous advantages compared to traditional drug delivery methods, including targeted delivery to specific sites, controlled release, and fewer side effects. This review meticulously examines the methodologies employed in the preparation and characterization of liposomal formulations. With the rising incidence of adverse drug reactions, there is a pressing need for innovative delivery strategies that prioritize selectivity, specificity, and safety. Nanomedicine promises to revolutionize diagnostics and treatments, addressing current limitations and improving disease management, including cancer, which remains a major global health challenge. This paper aims to conduct a comprehensive study on the interest of biomedical research regarding nanotechnology and its implications for further applications.
Keywords: bioavailability; cancer; liposomes; nanomedicine; nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Recent advances on liposomal nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization and biomedical applications.Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2017 Jun;45(4):788-799. doi: 10.1080/21691401.2017.1282496. Epub 2017 Feb 8. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28278586 Review.
-
Advancements in Liposomal Nanomedicines: Innovative Formulations, Therapeutic Applications, and Future Directions in Precision Medicine.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Jan 31;20:1213-1262. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S488961. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 39911259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanotechnology-based approaches for targeted drug delivery for the treatment of respiratory tract infections.J Biol Methods. 2024 Oct 23;11(4):e99010032. doi: 10.14440/jbm.2024.0065. eCollection 2024. J Biol Methods. 2024. PMID: 39839091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peptide-Functionalized Nanomedicine: Advancements in Drug Delivery, Diagnostics, and Biomedical Applications.Molecules. 2025 Mar 31;30(7):1572. doi: 10.3390/molecules30071572. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40286158 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanomedicine in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease: bypassing the blood-brain barrier with cutting-edge nanotechnology.Neurol Sci. 2025 Apr;46(4):1489-1507. doi: 10.1007/s10072-024-07871-4. Epub 2024 Dec 6. Neurol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39638950 Review.
Cited by
-
Cyclodextrin-Based Drug Delivery Systems for Depression: Improving Antidepressant Bioavailability and Targeted Central Nervous System Delivery.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Mar 10;17(3):355. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17030355. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40143019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into Liposomal and Gel-Based Formulations for Dermatological Treatments.Gels. 2025 Mar 26;11(4):245. doi: 10.3390/gels11040245. Gels. 2025. PMID: 40277680 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kondos N., Sneed K., Pathak Y. Recent Trends in Nano Drug Delivery Systems to Treat Cancers: With Special Focus on Liposomal Drug Delivery Systems. SciBase Oncol. 2024;2:1–7.
-
- Fernández-Barahona I., Muñoz-Hernando M., Ruiz-Cabello J., Herranz F., Pellico J. Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: An Alternative for Positive Contrast in Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Inorganics. 2020;8:28. doi: 10.3390/inorganics8040028. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

