Organic Moiety on Sn(IV) Does Matter for In Vitro Mode of Action: n Bu3Sn(IV) Compounds with Carboxylato N-Functionalized 2-Quinolones Induce Anoikis-like Cell Death in A375 Cells
- PMID: 39771508
- PMCID: PMC11679857
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16121529
Organic Moiety on Sn(IV) Does Matter for In Vitro Mode of Action: n Bu3Sn(IV) Compounds with Carboxylato N-Functionalized 2-Quinolones Induce Anoikis-like Cell Death in A375 Cells
Abstract
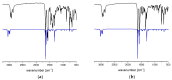
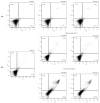
Objectives: New tributyltin(IV) complexes containing the carboxylate ligands 3-(4-methyl-2-oxoquinolin-1(2H)-yl)propanoic acid (HL1) and 2-(4-methyl-2-oxoquinolin-1(2H)-yl)acetic acid (HL2) have been synthesized. Methods: Their structures have been determined by elemental microanalysis, FT-IR and multinuclear NMR (1H, 13C and 119Sn) spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction study. A solution state NMR analysis reveals a four-coordinated tributyltin(IV) complex in non-polar solvents, while an X-Ray crystallographic analysis confirms a five-coordinated trigonal-bipyramidal geometry around the tin atom due to the formation of 1D chains. A theoretical structural analysis was performed by optimization employing B3LYP-D3BJ functional and 6-311++G(d,p)/def2-TZVP(Sn) basis sets for H, C, N, O/Sn, respectively. The interactions between tin(IV) and surrounding atoms were examined by QTAIM approach. The in vitro antiproliferative activity of the synthesized compounds was evaluated by MTT and CV assays versus MCF-7 (human breast adenocarcinoma), HCT116 (human colorectal carcinoma), A375 (human melanoma), 4T1 (mouse breast carcinoma), CT26 (mouse colon carcinoma) and B16 (mouse melanoma) tumor cell lines. Results: Both synthesized compounds (nBu3SnL1 and nBu3SnL2) exerted powerful micromolar IC50 cytotoxicity values and demonstrated high selectivity toward malignant cells. Both experimental drugs affected cell adhesion and induced anchorage independent apoptosis, a favorable type of cell death with an essential role in cancer dissemination prevention. The BSA-binding affinity of the obtained organotin compounds was followed by spectrofluorometric titration and molecular docking simulations. Conclusions: The tributyltin(IV) compounds selectively induce anoikis-like cell death in A375 cells, also highlighting the importance of the organic moiety on the tin(IV) ion in the mechanism of action.
Keywords: 2-quinolones; BSA interactions; apoptosis; in vitro cytotoxicity; molecular docking; tributyltin(IV) compounds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Cherek P., Balogova M., Damodaran K., Ögmundsdottir H.M. Abstract 2807: Cytotoxic Activity of Novel Organotin Compounds against Different Cancer Cell Lines. Cancer Res. 2018;78:2807. doi: 10.1158/1538-7445.AM2018-2807. - DOI
-
- Gielen M., Biesemans M., Willem R. Organotin Compounds: From Kinetics to Stereochemistry and Antitumour Activities. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2005;19:440–450. doi: 10.1002/aoc.771. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

