Innovative Nanomedicine Delivery: Targeting Tumor Microenvironment to Defeat Drug Resistance
- PMID: 39771528
- PMCID: PMC11728492
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16121549
Innovative Nanomedicine Delivery: Targeting Tumor Microenvironment to Defeat Drug Resistance
Abstract
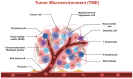
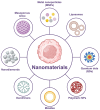
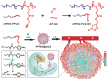
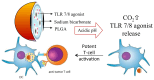
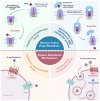
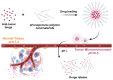
Nanodrug delivery systems have revolutionized tumor therapy like never before. By overcoming the complexity of the tumor microenvironment (TME) and bypassing drug resistance mechanisms, nanotechnology has shown great potential to improve drug efficacy and reduce toxic side effects. This review examines the impact of the TME on drug resistance and recent advances in nanomedicine delivery systems to overcome this challenge. Characteristics of the TME such as hypoxia, acidity, and high interstitial pressure significantly reduce the effectiveness of chemotherapy and radiotherapy, leading to increased drug resistance in tumor cells. Then, this review summarizes innovative nanocarrier designs for these microenvironmental features, including hypoxia-sensitive nanoparticles, pH-responsive carriers, and multifunctional nanosystems that enable targeted drug release and improved drug penetration and accumulation in tumors. By combining nanotechnology with therapeutic strategies, this review offers a novel perspective by focusing on the innovative design of nanocarriers that interact with the TME, a dimension often overlooked in similar reviews. We highlight the dual role of these nanocarriers in therapeutic delivery and TME modulation, emphasize their potential to overcome drug resistance, and look at future research directions.
Keywords: drug resistance; nanomedicine delivery; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Responsive Role of Nanomedicine in the Tumor Microenvironment and Cancer Drug Resistance.Curr Med Chem. 2023;30(29):3335-3355. doi: 10.2174/0929867329666220922111336. Curr Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36154585 Review.
-
T cell-mediated targeted delivery of tadalafil regulates immunosuppression and polyamine metabolism to overcome immune checkpoint blockade resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Immunother Cancer. 2023 Feb;11(2):e006493. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-006493. J Immunother Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36813307 Free PMC article.
-
Nanomedicine-Enhanced Radiotherapy for Glioblastoma: Advances in Targeted Therapy and Adaptive Treatment Strategies.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Apr 11;17(4):508. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17040508. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40284502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current advances in nanoformulations of therapeutic agents targeting tumor microenvironment to overcome drug resistance.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2023 Sep;42(3):959-1020. doi: 10.1007/s10555-023-10119-w. Epub 2023 Jul 28. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2023. PMID: 37505336 Review.
-
Tumor microenvironment-regulating nanomedicine design to fight multi-drug resistant tumors.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2023 Jan;15(1):e1842. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1842. Epub 2022 Aug 21. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2023. PMID: 35989568 Review.
Cited by
-
Circadian-Tuned Peptide Drug/Gene Co-Delivery Nanocomplexes to Enhance Glioblastoma Targeting and Transfection.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 26;26(13):6130. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136130. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40649908 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogenous cancer-associated fibroblasts related tumor microenvironment marked by CD10/KLF4/TIAM1 were identified in pancreatic adenocarcinoma by integrated transcriptomics.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 14;16:1557698. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1557698. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40303408 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-in-cell associated lncRNA signature predicts prognosis and immunotherapy response in gastric cancer.Front Oncol. 2025 Jul 8;15:1597187. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1597187. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40697378 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular markers for the efficacy of neoadjuvant immunotherapy for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2025 Jun 23;15:1586130. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1586130. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40626018 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effective imaging examination evaluation method for surgical pathological complete responds of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma after neoadjuvant immunochemotherapy.Front Oncol. 2025 Jun 10;15:1585194. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1585194. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40556669 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

