Polycystic Ovary Syndrome and the Potential for Nanomaterial-Based Drug Delivery in Therapy of This Disease
- PMID: 39771535
- PMCID: PMC11678845
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16121556
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome and the Potential for Nanomaterial-Based Drug Delivery in Therapy of This Disease
Abstract
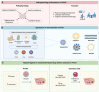
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is the predominant endocrine disorder among women of reproductive age and represents the leading cause of anovulatory infertility, which imposes a considerable health and economic burden. Currently, medications used to treat PCOS can lead to certain adverse reactions, such as affecting fertility and increasing the risk of venous thrombosis. Drug delivery systems utilizing nanomaterials, characterized by prolonged half-life, precision-targeted delivery, enhanced bioavailability, and reduced toxicity, are currently being employed in the management of PCOS. This innovative approach is gaining traction as a favored strategy for augmenting the therapeutic efficacy of medications. Consequently, this paper discusses the roles of nanoparticles, nanocarriers, and targeted ligands within nanomaterial-based drug delivery systems, aiming to identify optimal methodologies for treating PCOS using nanomaterials. Additionally, prospective research avenues concerning nanomaterial-based delivery systems in the context of PCOS, as well as the implications of existing insights on the advancement of novel therapies for PCOS, are highlighted.
Keywords: nanoparticles; novel drug delivery systems; polycystic ovary syndrome; therapeutic efficacy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Mills G., Badeghiesh A., Suarthana E., Baghlaf H., Dahan M.H. Polycystic ovary syndrome as an independent risk factor for gestational diabetes and hypertensive disorders of pregnancy: A population-based study on 9.1 million pregnancies. Hum. Reprod. 2020;35:1666–1674. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deaa099. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Teede H.J., Tay C.T., Laven J., Dokras A., Moran L.J., Piltonen T.T., Costello M.F., Boivin J., Redman L.M., Boyle J.A., et al. Recommendations from the 2023 International Evidence-based Guideline for the Assessment and Management of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Hum. Reprod. 2023;38:1655–1679. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dead156. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
- 82374425/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82160923/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82460974/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 202301AS070053/Applied Basic Research Programs of Science and Technology Commission Foundation of Yunnan Province
- Yunnan Provincial Department of Education/Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine for Prevention and Treatment of Neuropsychi-atric Diseases
- 2019YZG01/Scientific Research Projects for High-level Talents of Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine
- YNWR-QNBJ-2019-235/Young Top-Notch Talent in 10,000 Talent Program of Yunnan Province
- 202405AS350007/Yunnan Province Innovation Team of Prevention and Treatment for Brain Diseases With Acu-puncture and Tuina
- 2024SS24007/Yunnan Key Laboratory of Dai and Yi Medicines ,Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

