Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Fexofenadine: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 39771597
- PMCID: PMC11677975
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16121619
Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Fexofenadine: A Systematic Review
Abstract
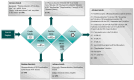
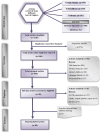
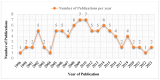
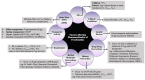
Background/Objectives: Fexofenadine hydrochloride is a widely prescribed drug for treating histamine-mediated allergic reactions. This review systematically collates existing research on the clinical pharmacokinetics (PK) of fexofenadine, with a copious emphasis on examining the impact of stereoisomerism, disease states, and drug interactions. Methods: The search engines PubMed, Science Direct, Google Scholar, and Cochrane were scanned systematically for articles concerning the clinical PK of fexofenadine in humans. The extensive literature search yielded 85 articles meeting the inclusion standards. Results: The PK parameters of fexofenadine showed a linear correlation between increasing doses and proportional elevations in PK parameters such as area under the curve from time 0 to infinity (AUC0-∞) and maximum plasma concentration (Cmax). Under fed conditions, its bioavailability was reduced by approximately 50%. Findings from patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) displayed a 63% decline in oral clearance (CL/F) of fexofenadine. A drug-food interaction study has displayed that grapefruit juice decreased Cmax (201 ng/mL vs. 128 ng/mL), accompanied by a 30% reduction in the bioavailability of fexofenadine. Furthermore, a drug-herb interaction study with St John's Wort (SJW) has reported a reduction in CL/F by 10% after a single dose, but long-term administration reversed this effect, resulting in elevated CL/F by 17% of fexofenadine. Conclusions: Since no prior systematic review on the PK of this drug exists, this review amalgamates all pertinent PK parameters in humans by pooling up-to-date data from published studies. This detailed literature review can be advantageous for researchers who want to develop and assess PK models.
Keywords: AUC; allergic rhinitis; clearance; fexofenadine; humans; pharmacokinetics; second generation; systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest that might be relevant to the contents of this manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Handley D.A. Advancement of the Third Generation of Antihistamines. Pediatr. Asthma Allergy Immunol. 1999;13:163–168. doi: 10.1089/pai.1999.13.163. - DOI
-
- Fischer J., Ganellin C.R. Analogue-based drug discovery. Chem. Int. Newsmag. IUPAC. 2010;32:12–15.
-
- Asha P.K., Raghu M.S., Devi V.S.A. Properties of Potassium Permanganate as Oxidant in the Determination of Fexofenadine in Pharmaceuticals. Sens. Lett. 2020;18:64–68. doi: 10.1166/sl.2020.4190. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources