Cationic Hydroxyethyl Cellulose Nanocomplexes and RANK siRNA/Zoledronate Co-Delivery Systems for Osteoclast Inhibition
- PMID: 39771601
- PMCID: PMC11679713
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16121623
Cationic Hydroxyethyl Cellulose Nanocomplexes and RANK siRNA/Zoledronate Co-Delivery Systems for Osteoclast Inhibition
Abstract
Background/objectives: In this study, HECP2k polymer, polyethylenimine2k (PEI2k)-modified hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC) was utilized to form the nanocomplexes with receptor activator of nuclear factor k-B (RANK) siRNA and zoledronate (Zol) for osteoclast inhibition. HECP2k/(RANK siRNA + Zol) nanocomplexes prepared by simple mixing were anticipated to overcome the low transfection efficiency of siRNA and the low bioavailability of Zol.
Methods: The characterization of both HECP2k/(pDNA + Zol) nanocomplexes and HECP2k/(RANK siRNA + Zol) nanocomplexes was performed.
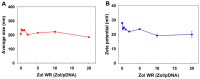
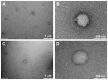
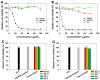
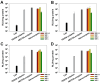
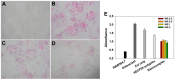
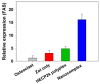
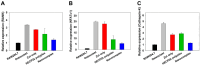
Results: The nanocomplexes were successfully formed even in the presence of Zol, showing about 200 nm sizes and about 20 mV of positive zeta potential values suitable for efficient cellular uptake. They also possessed high endosome buffering ability by PEI and Zol, suggesting the potential for efficient endosomal escape. It was found that the low cytotoxic nanocomplexes (>90% cell viability) displayed greater transfection efficiency than PEI25k and even HECP2k polyplexes. Finally, it was found by tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) assay and qPCR analysis that HECP2k/(RANK siRNA + Zol) nanocomplexes could inhibit the TRAP to about 50% value and another characteristic osteoclastic gene expression, increasing FAS gene expression to about 16 times higher than control and more efficiently (about 3 times and 5 times higher, respectively) than HECP2k/siRNA polyplexes and Zol only.
Conclusions: HECP2k/(RANK siRNA + Zol) nanocomplexes formed by simple mixing showed great potential for inhibiting osteoclast differentiation and osteoclast activity, inducing the apoptosis via combinatorial effects of RANK siRNA and Zol.
Keywords: RANK siRNA; drug/gene co-delivery systems; hydroxyethyl cellulose; nanocomplex; osteoclast inhibition; zoledronate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

