Twin Screw Melt Granulation of Simvastatin: Drug Solubility and Dissolution Rate Enhancement Using Polymer Blends
- PMID: 39771607
- PMCID: PMC11678365
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16121630
Twin Screw Melt Granulation of Simvastatin: Drug Solubility and Dissolution Rate Enhancement Using Polymer Blends
Abstract
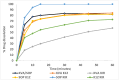
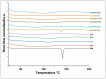
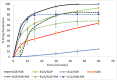
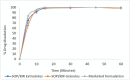
Background/Objectives: This study evaluates the efficacy of twin screw melt granulation (TSMG), and hot-melt extrusion (HME) techniques in enhancing the solubility and dissolution of simvastatin (SIM), a poorly water-soluble drug with low bioavailability. Additionally, the study explores the impact of binary polymer blends on the drug's miscibility, solubility, and in vitro release profile. Methods: SIM was processed with various polymeric combinations at a 30% w/w drug load, and a 1:1 ratio of binary polymer blends, including Soluplus® (SOP), Kollidon® K12 (K12), Kollidon® VA64 (KVA), and Kollicoat® IR (KIR). The solid dispersions were characterized using modulated differential scanning calorimetry (M-DSC), powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD), and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). Dissolution studies compared the developed formulations against a marketed product. Results: The SIM-SOP/KIR blend showed the highest solubility (34 µg/mL), achieving an approximately 5.5-fold enhancement over the pure drug. Dissolution studies showed that SIM-SOP/KIR formulations had significantly higher release profiles than the physical mixture (PM) and pure drug (p < 0.01). Additionally, their release was similar to a marketed formulation, with 100% drug release within 30 min. In contrast, the SIM-K12/KIR formulation exhibited strong miscibility, but limited solubility and slower release rates, suggesting that high miscibility does not necessarily correlate with improved solubility. Conclusions: This study demonstrates the effectiveness of TSMG, and HME as effective continuous manufacturing technologies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of poorly water-soluble drugs. It also emphasizes the complexity of polymer-drug interactions and the necessity of carefully selecting compatible polymers to optimize the quality and performance of pharmaceutical formulations.
Keywords: Kollicoat IR; Soluplus; amorphous solid dispersion; hot-melt extrusion; miscibility; poorly water-soluble drug; solubility enhancement; twin screw melt granulation.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Krizia Karry was employed by the company BASF. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- ZOCOR®. [(accessed on 17 December 2024)]; Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2023/019766s104lbl.pdf.
-
- Saoji S.D., Belgamwar V.S., Dharashivkar S.S., Rode A.A., Mack C., Dave V.S. The Study of the Influence of Formulation and Process Variables on the Functional Attributes of Simvastatin–Phospholipid Complex. J. Pharm. Innov. 2016;11:264–278. doi: 10.1007/s12247-016-9256-7. - DOI
-
- Bolla N., Chandra S., Raju R., Rao K., Devi U. Improvement of Simvastatin Solubility Using Natural Polymers by solid dispersion technique. Int. J. Pharm. Res. Biomed. Anal. 2013;2:1–6.
-
- Nandi U., Ajiboye A.L., Patel P., Douroumis D., Trivedi V. Preparation of solid dispersions of simvastatin and soluplus using a single-step organic solvent-free supercritical fluid process for the drug solubility and dissolution rate enhancement. Pharmaceuticals. 2021;14:846. doi: 10.3390/ph14090846. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

