Systematic Review of EEG-Based Imagined Speech Classification Methods
- PMID: 39771903
- PMCID: PMC11679664
- DOI: 10.3390/s24248168
Systematic Review of EEG-Based Imagined Speech Classification Methods
Abstract
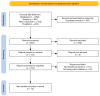
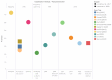
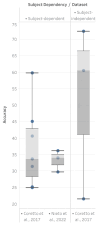
This systematic review examines EEG-based imagined speech classification, emphasizing directional words essential for development in the brain-computer interface (BCI). This study employed a structured methodology to analyze approaches using public datasets, ensuring systematic evaluation and validation of results. This review highlights the feature extraction techniques that are pivotal to classification performance. These include deep learning, adaptive optimization, and frequency-specific decomposition, which enhance accuracy and robustness. Classification methods were explored by comparing traditional machine learning with deep learning and emphasizing the role of brain lateralization in imagined speech for effective recognition and classification. This study discusses the challenges of generalizability and scalability in imagined speech recognition, focusing on subject-independent approaches and multiclass scalability. Performance benchmarking across various datasets and methodologies revealed varied classification accuracies, reflecting the complexity and variability of EEG signals. This review concludes that challenges remain despite progress, particularly in classifying directional words. Future research directions include improved signal processing techniques, advanced neural network architectures, and more personalized, adaptive BCI systems. This review is critical for future efforts to develop practical communication tools for individuals with speech and motor impairments using EEG-based BCIs.
Keywords: BCI; EEG; brain–computer interfaces; electroencephalogram; imagined speech; inner speech.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Keiper A. The age of neuroelectronics. New Atlantis. 2006;11:4–41. - PubMed
-
- Vorontsova D., Menshikov I., Zubov A., Orlov K., Rikunov P., Zvereva E., Flitman L., Lanikin A., Sokolova A., Markov S., et al. Silent EEG-Speech Recognition Using Convolutional and Recurrent Neural Network with 85% Accuracy of 9 Words Classification. Sensors. 2021;21:6744. doi: 10.3390/s21206744. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- García A.A.T., García C.A.R., Villaseñor-Pineda L., García G. Implementing a fuzzy inference system in a multi-objective EEG channel selection model for imagined speech classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016;59:1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2016.04.011. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

