Advancements in Nanoparticle-Based Adjuvants for Enhanced Tuberculosis Vaccination: A Review
- PMID: 39771997
- PMCID: PMC11680411
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines12121335
Advancements in Nanoparticle-Based Adjuvants for Enhanced Tuberculosis Vaccination: A Review
Abstract
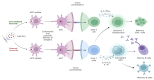
Tuberculosis (TB) remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, necessitating the development of more effective vaccines. Nanoparticle-based adjuvants represent a promising approach to enhancing tuberculosis vaccine efficacy. This review focuses on the advantages of nanoparticulate-loaded vaccines, emphasizing their ability to improve antigen delivery, safety, and immunogenicity. We discuss the various types of nanoparticles and their unique physicochemical properties that contribute to improved antigen delivery and sustained immune activation. Additionally, we highlight the advantages of nanoparticle-based adjuvants in inducing strong cellular and humoral immunity, enhancing vaccine stability, and reducing adverse effects. Finally, we address current challenges and future perspectives in the application of these novel adjuvants, emphasizing their potential to transform TB vaccine strategies and ultimately contribute to better global health outcomes.
Keywords: adjuvants; nanoparticles; tuberculosis; vaccines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
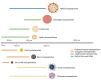
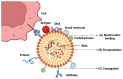
References
-
- Bekale R.B., Du Plessis S.-M., Hsu N.-J., Sharma J.R., Sampson S.L., Jacobs M., Meyer M., Morse G.D., Dube A. Mycobacterium Tuberculosis and Interactions with the Host Immune System: Opportunities for Nanoparticle Based Immunotherapeutics and Vaccines. Pharm. Res. 2018;36:8. doi: 10.1007/s11095-018-2528-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Marks S.M., Flood J., Seaworth B., Hirsch-Moverman Y., Armstrong L., Mase S., Salcedo K., Oh P., Graviss E.A., Colson P.W. Treatment practices, outcomes, and costs of multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis, United States, 2005–2007. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014;20:812. doi: 10.3201/eid2005.131037. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

