Advances in Vaccine Adjuvants for Teleost Fish: Implications for Aquatic Welfare and the Potential of Nanoparticle-Based Formulations
- PMID: 39772009
- PMCID: PMC11679523
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines12121347
Advances in Vaccine Adjuvants for Teleost Fish: Implications for Aquatic Welfare and the Potential of Nanoparticle-Based Formulations
Abstract
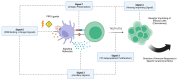
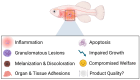
Vaccine adjuvants are crucial for reinforcing the immunogenicity of vaccines. Therefore, they are widely used in the aquaculture sector as vaccine components, facilitating the efficient prevention of infectious diseases and promoting sustainable teleost fish growth. Despite their benefits, there has been a growing concern about the potential adverse effects of vaccine adjuvants in teleost fish, connoting a valid impact on their overall health and welfare. Among the adjuvants used in aquaculture vaccinology, nanoparticle-based formulations have given rise to a promising new alternative to traditional options, such as oil-based emulsions and aluminum compounds, offering the benefit of minimizing relevant side effects. The aim of this paper was to review the current status of the adjuvants used in aquaculture, provide a description and an evaluation of their mode of action and side effects, and explore the potential use of nanoparticle formulations as adjuvants to improve the efficacy of aquaculture vaccines. By demonstrating and assessing the equilibrium between teleost fish welfare and immunological efficacy, this review presents a collective perspective that will assist in establishing a framework for the utilization of effective species-specific practices around adjuvant use in aquaculture, while also addressing the challenges of welfare-friendly immunization.
Keywords: adjuvants; aquaculture; granulomas; health; immunization; inflammation; lesions; nanoparticles; side effects; sustainability; teleost fish; vaccines; welfare.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Advances and Challenges in Aeromonas hydrophila Vaccine Development: Immunological Insights and Future Perspectives.Vaccines (Basel). 2025 Feb 18;13(2):202. doi: 10.3390/vaccines13020202. Vaccines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40006748 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adjuvants and immunostimulants in fish vaccines: current knowledge and future perspectives.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013 Dec;35(6):1740-50. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2013.02.029. Epub 2013 Mar 16. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23507338 Review.
-
Transforming Aquaculture through Vaccination: A Review on Recent Developments and Milestones.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Jul 1;12(7):732. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12070732. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39066370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Salmonid Antibacterial Immunity: An Aquaculture Perspective.Biology (Basel). 2020 Oct 11;9(10):331. doi: 10.3390/biology9100331. Biology (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33050557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative study of the effects of Montanide™ ISA 763A VG and ISA 763B VG adjuvants on the immune response against Streptococcus agalactiae in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus).Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023 Mar;134:108563. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2023.108563. Epub 2023 Jan 27. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36717067
Cited by
-
Advances and Challenges in Aeromonas hydrophila Vaccine Development: Immunological Insights and Future Perspectives.Vaccines (Basel). 2025 Feb 18;13(2):202. doi: 10.3390/vaccines13020202. Vaccines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40006748 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Vincent A.T., Gauthier J., Derome N., Charette S.J. The Rise and Fall of Antibiotics in Aquaculture. In: Derome N., editor. Microbial Communities in Aquaculture Ecosystems: Improving Productivity and Sustainability. Springer International Publishing; Cham, Switzerland: 2019. pp. 1–19.
-
- Arechavala-Lopez P., Sanchez-Jerez P., Bayle-Sempere J.T., Uglem I., Mladineo I. Reared Fish, Farmed Escapees and Wild Fish Stocks—A Triangle of Pathogen Transmission of Concern to Mediterranean Aquaculture Management. Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2013;3:153–161. doi: 10.3354/aei00060. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

