Longitudinal Comparison of Three T-Cell Assays and Three Antibody Assays Against SARS-CoV-2 Following Homologous mRNA-1273/mRNA-1273/mRNA-1273 and Heterologous ChAdOx1/ChAdOx1/BNT162b2 Vaccination: A Prospective Cohort in Naïve Healthcare Workers
- PMID: 39772013
- PMCID: PMC11679843
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines12121350
Longitudinal Comparison of Three T-Cell Assays and Three Antibody Assays Against SARS-CoV-2 Following Homologous mRNA-1273/mRNA-1273/mRNA-1273 and Heterologous ChAdOx1/ChAdOx1/BNT162b2 Vaccination: A Prospective Cohort in Naïve Healthcare Workers
Abstract
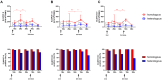
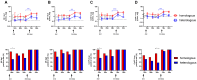
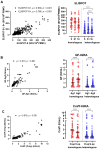
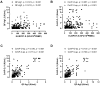
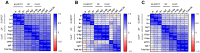
Background: Cellular and humoral immunity are key to the immune response against SARS-CoV-2, but the comparability and correlation across different assays remain underexplored. This study compares three T-cell and three antibody assays in two vaccine groups. Methods: This prospective longitudinal cohort study involved 46 naïve healthcare workers: a total of 11 in the homologous mRNA-1273 group (three doses) and 35 in the heterologous ChAd group (two ChAd doses followed by a BNT booster). Blood samples were collected at five time points. Cellular immunity was assessed using ELISPOT and two commercial interferon-gamma release assays: (IGRA)-QuantiFERON SARS-CoV-2 (QF) and Covi-FERON ELISA (CoVF). Humoral immunity was evaluated using total and IgG antibody assays and a surrogate virus neutralization test. Results: The mRNA-1273 group exhibited stronger and more consistent responses than the ChAd group. The correlations between ELISPOT and IGRA varied from weak to moderate (ρ = 0.300-0.410), while QF-IGRA and CoVF-IGRA showed stronger correlations (ρ = 0.700-0.737). The ELISPOT assay showed substantial agreement with QF [Ag2]-IGRA (k = 0.697-0.774) and CoVF [O-sp]-IGRA (k = 0.641-0.718), and an 80.4% agreement rate (k = 0.608) was found between the QF [Ag2]- and CoVF [O-sp]-IGRA tests. Three antibody assays demonstrated very strong correlations with each other and substantial to near-perfect agreement with ELISPOT (k = 0.866-0.949), QF [Ag2]-IGRA (k = 0.807-0.831), and CoVF [O-sp]-IGRA (k = 0.753-0.777). Conclusions: SARS-CoV-2-specific cellular and antibody responses vary by platform and vaccine type, highlighting the importance of measuring both T-cell and B-cell responses using multiple assays to comprehensively assess immune status.
Keywords: ELISPOT; SARS-CoV-2; cellular response; humoral response; interferon-gamma release assay; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. SD biosensor (Korea) had no role in the design of this study, data collection, data analyses, data interpretation, writing of the manuscript, or decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
-
- Ssentongo P., Ssentongo A.E., Voleti N., Groff D., Sun A., Ba D.M., Nunez J., Parent L.J., Chinchilli V.M., Paules C.I. SARS-CoV-2 vaccine effectiveness against infection, symptomatic and severe COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2022;22:439. doi: 10.1186/s12879-022-07418-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen Y., Chen L., Yin S., Tao Y., Zhu L., Tong X., Mao M., Li M., Wan Y., Ni J., et al. The Third dose of CoronVac vaccination induces broad and potent adaptive immune responses that recognize SARS-CoV-2 Delta and Omicron variants. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022;11:1524–1536. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2022.2081614. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

