A Preclinical Immunogenicity Study of the Recombinant Human Papillomavirus Nine-Valent Virus-like Particle Vaccine
- PMID: 39772018
- PMCID: PMC11680239
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines12121356
A Preclinical Immunogenicity Study of the Recombinant Human Papillomavirus Nine-Valent Virus-like Particle Vaccine
Abstract
Background: Cervical cancer is associated with persistent infection of high-risk human papillomaviruses (HPVs). Prophylactic HPV vaccines have been recommended and have significant efficacy in preventing cervical cancer. Multivalent HPV vaccines have a better preventative effect on HPV-related diseases. However, there is currently only one nine-valent HPV vaccine on the market: Gardasil® 9. The development of new HPV vaccines is still urgent in order to achieve the goal of eliminating cervical cancer as proposed by the WHO.
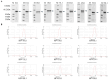
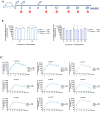
Methods: In this study, we developed a nine-valent recombinant HPV virus-like particle (VLP) vaccine (HPV-9 vaccine) containing HPV type 6, 11, 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 52, and 58 antigens, with an adjuvant of aluminum phosphate (AlPO4). The type-specific L1 proteins were recombinantly expressed using Pichia pastoris, followed by self-assembly into VLPs. Immunogenicity studies of the HPV-9 vaccine were performed using rodents (mice and rats) and non-human primates (macaques) as animal models.
Results: Immunogenicity studies showed that the HPV-9 vaccine is able to elicit a robust and long-lasting neutralizing antibody response in rodents (mice and rats) and non-human primates (cynomolgus macaque) models. The HPV-9 vaccine shows immunogenicity comparable to that of Walrinvax® and Gardasil® 9.
Conclusions: In summary, this study provides a comprehensive investigation of the immunogenicity of the HPV-9 vaccine, including its immune persistence. These findings, derived from using models of diverse animal species, contribute valuable insights into the potential efficacy of the vaccine candidate in clinical settings.
Keywords: human papillomavirus (HPV); immunogenicity; protective efficacy; vaccines; virus-like particles (VLPs).
Conflict of interest statement
D.X., J.-D.L., J.A., X.-X.M., X.-L.W., Z.Z., H.-P.L., M.-J.D., Y.-X.J., L.-Y.Z., and C.-L.Z. are employees of Shanghai Zerun Biotech Co., Ltd. X.T. is a former employee of Shanghai Zerun Biotech Co., Ltd. and currently works at Yunnan Walvax Biotech Co., Ltd., which is the holding company of Shanghai Zerun Biotech Co., Ltd.
Figures



References
-
- Cervical Cancer. [(accessed on 17 November 2020)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/cervical-cancer#tab=tab_2.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

