Evaluation of the Efficacy of the Vaccine Production Process in Removing Residual Host Cell DNA from the Vero Cell Rabies Vaccine
- PMID: 39772041
- PMCID: PMC11680306
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines12121379
Evaluation of the Efficacy of the Vaccine Production Process in Removing Residual Host Cell DNA from the Vero Cell Rabies Vaccine
Abstract
Background: The Vero cell rabies vaccine is currently the most widely used human rabies vaccine. However, owing to the presence of residual host cell DNA (HCD) in the final product and the potential tumorigenicity of the DNA of high-passage Vero cells, the WHO not only sets a limit on the number of times cells used in production can be passaged, but also imposes strict requirements on the amount of residual HCD in the final vaccine product.
Objectives: To systematically reduce the HCD level in the final vaccine product, multiple purification steps are included in the vaccine production process. This study investigated the effectiveness of key production steps in antigen recovery and DNA removal.
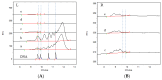
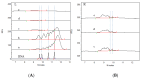
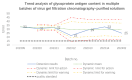
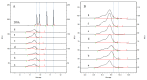
Methods: The residual HCD fragment content and size distribution were detected using fluorescence quantitative PCR (qPCR) and capillary gel electrophoresis (CGE), and the rabies virus glycoprotein antigen content was detected using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The antigen recovery rate and HCD removal rate in each key process were calculated to evaluate the scientific basis and effectiveness of each production step. Additionally, the stability of the process was studied using multiple commercial batches of the product.
Results: The results revealed that the total antigen recovery rate in the production process described in this report was no less than 8.5%, and the effective removal rate of residual HCD was not lower than 99.99%. Moreover, the amount of residual HCD in the final product was far below the quality standard of 2 ng/dose, and most of the residual HCD fragments were smaller than 200 bp. The results of the process stability studies on multiple commercial batches showed that the bulk human rabies vaccine produced by this process had excellent safety and efficacy and that the production process was stable and thus suitable for large-scale batch production.
Conclusions: The production process described in this study achieved effective recovery of viral antigens and efficient removal of residual HCD, and the process was stable and controllable, enabling the continuous and stable production of vaccine products that meet WHO recommendations and the relevant requirements of the current edition of the Chinese Pharmacopeia. In addition, this study provides theoretical guidance for optimizing the vaccine production process.
Keywords: DNA fragment size distribution; HCD removal; Vero cells; rabies virus.
Conflict of interest statement
Tie Gao, Zhaohui Lan and Hongxu Chen are employed by SCIEX, Ruowen Pan and Fengyi Yue are employed by Hualan Biological Vaccine Inc. The remianing authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Yasumura Y., Kawakita Y. Studies on SV40 in tissue culture: Preliminary step for cancer research in vitro. Nihon Rinsho. 1963;21:1201–1215. (In Japanese)
-
- Sheng L., Cai F., Zhu Y., Pal A., Athanasiou M., Orrison B., Blair D.G., Hughes S.H., Coffin J.M., Lewis A.M., et al. Oncogenicity of DNA in vivo: Tumor induction with expression plasmids for activated H-ras and c-myc. Biol. J. Int. Assoc. Biol. Stand. 2008;36:184–197. doi: 10.1016/j.biologicals.2007.11.003. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

