Cell-Cultured Influenza Vaccine Enhances IFN-γ+ T Cell and Memory T Cell Responses Following A/Victoria/2570/2019 IVR-215 (A/H1N1) Infection
- PMID: 39772053
- PMCID: PMC11680451
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines12121392
Cell-Cultured Influenza Vaccine Enhances IFN-γ+ T Cell and Memory T Cell Responses Following A/Victoria/2570/2019 IVR-215 (A/H1N1) Infection
Abstract
Background: Influenza remains a significant public health challenge, with vaccination being a substantial way to prevent it. Cell-cultured influenza vaccines have emerged to improve on the drawbacks of egg-based vaccines, but there are few studies focusing on T cell immunity with both types of vaccines. Therefore, we studied the following 2022-2023 seasonal influenza vaccines with a standard dose and high dose: cell-based (C_sd and C_hd) and egg-based (E_sd and E_hd) vaccines.
Methods: Along with a saline control group, C_sd, C_hd, E_sd, and E_hd vaccines were administered to BALB/c mice, followed by a challenge with the A/Victoria/2570/2019 (H1N1) strain.
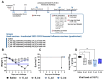
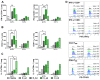
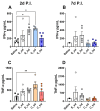
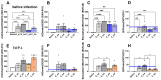
Results: After the challenge, four out of five mice in the saline group died by day 7 post-infection (P.I.). None of the vaccinated groups experienced over 20% weight loss or any deaths. On day 7 P.I., the lung viral load in the saline group (mean log value of 4.17) was higher than that in the vaccinated groups, with the C_sd group showing the lowest viral load (mean log value of 3.47). The C_sd group showed a significantly high response in macrophage 1 (M1), IFN-γ+ T cells, and tissue-resident memory (TRM) T cells compared with the E_sd group on day 2 P.I. These M1, IFN-γ+ T cells, and TRM cells showed similar trends (p < 0.01). In terms of humoral immunity, only the E_hd group showed HAI titers above 40 for all four strains before and after the challenge.
Conclusions: The high levels of T cells in the cell-cultured vaccines suggest, pending further real-world research, that these vaccines may offer advantages.
Keywords: T cells in influenza vaccine immunity; cell-cultured influenza vaccine; egg-based influenza vaccine; immune cells in influenza vaccine immunity; influenza vaccine efficacy.
Conflict of interest statement
P.-K.K., K.-M.J. and J.-Y.J. are employees of SK Bioscience. While every effort has been made to ensure the integrity and objectivity of the research, the potential for perceived or actual conflicts of interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Dawood F.S., Iuliano A.D., Reed C., Meltzer M.I., Shay D.K., Cheng P.-Y., Bandaranayake D., Breiman R.F., Brooks W.A., Buchy P., et al. Estimated global mortality associated with the first 12 months of 2009 pandemic influenza A H1N1 virus circulation: A modelling study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2012;12:687–695. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(12)70121-4. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

