Photophysics-informed two-photon voltage imaging using FRET-opsin voltage indicators
- PMID: 39772682
- PMCID: PMC11708879
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adp5763
Photophysics-informed two-photon voltage imaging using FRET-opsin voltage indicators
Abstract
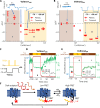
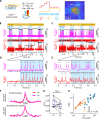
Microbial rhodopsin-derived genetically encoded voltage indicators (GEVIs) are powerful tools for mapping bioelectrical dynamics in cell culture and in live animals. Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET)-opsin GEVIs use voltage-dependent quenching of an attached fluorophore, achieving high brightness, speed, and voltage sensitivity. However, the voltage sensitivity of most FRET-opsin GEVIs has been reported to decrease or vanish under two-photon (2P) excitation. Here, we investigated the photophysics of the FRET-opsin GEVIs Voltron1 and Voltron2. We found that the previously reported negative-going voltage sensitivities of both GEVIs came from photocycle intermediates, not from the opsin ground states. The voltage sensitivities of both GEVIs were nonlinear functions of illumination intensity; for Voltron1, the sensitivity reversed the sign under low-intensity illumination. Using photocycle-optimized 2P illumination protocols, we demonstrate 2P voltage imaging with Voltron2 in the barrel cortex of a live mouse. These results open the door to high-speed 2P voltage imaging of FRET-opsin GEVIs in vivo.
Figures


Update of
-
Photophysics-informed two-photon voltage imaging using FRET-opsin voltage indicators.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 2:2024.04.01.587540. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.01.587540. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Sci Adv. 2025 Jan 10;11(2):eadp5763. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adp5763. PMID: 38617370 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Adam Y., All-optical electrophysiology in behaving animals. J. Neurosci. Methods 353, 109101 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Abdelfattah A. S., Zheng J., Singh A., Huang Y.-C., Reep D., Tsegaye G., Tsang A., Arthur B. J., Rehorova M., Olson C. V. L., Shuai Y., Zhang L., Fu T.-M., Milkie D. E., Moya M. V., Weber T. D., Lemire A. L., Baker C. A., Falco N., Zheng Q., Grimm J. B., Yip M. C., Walpita D., Chase M., Campagnola L., Murphy G. J., Wong A. M., Forest C. R., Mertz J., Economo M. N., Turner G. C., Koyama M., Lin B.-J., Betzig E., Novak O., Lavis L. D., Svoboda K., Korff W., Chen T.-W., Schreiter E. R., Hasseman J. P., Kolb I., Sensitivity optimization of a rhodopsin-based fluorescent voltage indicator. Neuron 111, 1547–1563.e9 (2023). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Adam Y., Kim J. J., Lou S., Zhao Y., Xie M. E., Brinks D., Wu H., Mostajo-Radji M. A., Kheifets S., Parot V., Chettih S., Williams K. J., Gmeiner B., Farhi S. L., Madisen L., Buchanan E. K., Kinsella I., Zhou D., Paninski L., Harvey C. D., Zeng H., Arlotta P., Campbell R. E., Cohen A. E., Voltage imaging and optogenetics reveal behaviour-dependent changes in hippocampal dynamics. Nature 569, 413–417 (2019). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kralj J. M., Hochbaum D. R., Douglass A. D., Cohen A. E., Electrical spiking in Escherichia coli probed with a fluorescent voltage indicating protein. Science 333, 345–348 (2011). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

