Large stroke radially oriented MXene composite fiber tensile artificial muscles
- PMID: 39772688
- PMCID: PMC11708897
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adt1560
Large stroke radially oriented MXene composite fiber tensile artificial muscles
Abstract
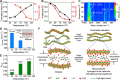
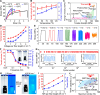
Actuation is normally dramatically enhanced by introducing so much yarn fiber twist that the fiber becomes fully coiled. In contrast, we found that usefully high muscle strokes and contractile work capacities can be obtained for non-twisted MXene (Ti3C2Tx) fibers comprising MXene nanosheets that are stacked in the fiber direction. The MXene fiber artificial muscles are called MFAMs. We obtained MFAMs that have high modulus in both the radial and axial directions by spinning a solution containing MXene nanosheets dispersed in an aqueous cellulose solution. We observed a highly reversible muscle contraction of 21.0% for a temperature increase from 25° to 125°C. The tensile actuation of MFAMs mainly results from reversible hydrogen bond orientation change during heating, which decreases intra-sheet spacing. The MFAMs exhibited fast, stable actuation to multiple temperature-generating stimuli, which increases their applications in smart textiles, robotic arms, and robotic grippers.
Figures


References
-
- Leng X., Mei G., Zhang G., Liu Z., Zhou X., Tethering of twisted-fiber artificial muscles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 57, 2377–2390 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Roach D. J., Yuan C., Kuang X., Li V. C.-F., Blake P., Romero M. L., Hammel I., Yu K., Qi H. J., Long liquid crystal elastomer fibers with large reversible actuation strains for smart textiles and artificial muscles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 19514–19521 (2019). - PubMed
-
- He Q., Wang Z., Wang Y., Wang Z., Li C., Annapooranan R., Zeng J., Chen R., Cai S., Electrospun liquid crystal elastomer microfiber actuator. Sci. Robot. 6, eabi9704 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Yang D., Feng M., Gu G., High-stroke, high-output-force, fabric-lattice artificial muscles for soft robots. Adv. Mater. 36, e2306928 (2023). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

