Virtual Gram staining of label-free bacteria using dark-field microscopy and deep learning
- PMID: 39772690
- PMCID: PMC11803577
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.ads2757
Virtual Gram staining of label-free bacteria using dark-field microscopy and deep learning
Abstract
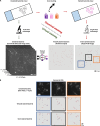
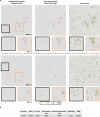
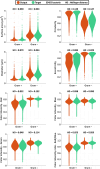
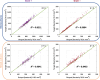
Gram staining has been a frequently used staining protocol in microbiology. It is vulnerable to staining artifacts due to, e.g., operator errors and chemical variations. Here, we introduce virtual Gram staining of label-free bacteria using a trained neural network that digitally transforms dark-field images of unstained bacteria into their Gram-stained equivalents matching bright-field image contrast. After a one-time training, the virtual Gram staining model processes an axial stack of dark-field microscopy images of label-free bacteria (never seen before) to rapidly generate Gram staining, bypassing several chemical steps involved in the conventional staining process. We demonstrated the success of virtual Gram staining on label-free bacteria samples containing Escherichia coli and Listeria innocua by quantifying the staining accuracy of the model and comparing the chromatic and morphological features of the virtually stained bacteria against their chemically stained counterparts. This virtual bacterial staining framework bypasses the traditional Gram staining protocol and its challenges, including stain standardization, operator errors, and sensitivity to chemical variations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A novel framework for the automated characterization of Gram-stained blood culture slides using a large-scale vision transformer.J Clin Microbiol. 2025 Mar 12;63(3):e0151424. doi: 10.1128/jcm.01514-24. Epub 2025 Feb 24. J Clin Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39992156 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement of gram staining effect by ethanol pretreatment and quantization of staining image by unsupervised machine learning.Arch Microbiol. 2024 Jun 21;206(7):318. doi: 10.1007/s00203-024-04045-w. Arch Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38904719
-
Automated Interpretation of Blood Culture Gram Stains by Use of a Deep Convolutional Neural Network.J Clin Microbiol. 2018 Feb 22;56(3):e01521-17. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01521-17. Print 2018 Mar. J Clin Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29187563 Free PMC article.
-
Virtual staining for histology by deep learning.Trends Biotechnol. 2024 Sep;42(9):1177-1191. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2024.02.009. Epub 2024 Mar 13. Trends Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38480025 Review.
-
Microwave-accelerated cytochemical stains for the image analysis and the electron microscopic examination of light microscopy diagnostic slides.Scanning. 1993 Mar-Apr;15(2):67-80. doi: 10.1002/sca.4950150203. Scanning. 1993. PMID: 7506980 Review.
References
-
- Gram H. C., Ueber die isolirte Farbung der Schizomyceten in Schnitt-und Trockenpraparaten. Fortschritte der Medicin 2, 185–189 (1884).
-
- B. B. Biswas, P. S. Basu, M. K. Pal, Gram Staining and Its Molecular Mechanism, in International Review of Cytology, G. H. Bourne, J. F. Danielli, K. W. Jeon, Eds. (Academic Press, 1970), vol. 29, pp. 1–27. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0074769608600315. - PubMed
-
- Beveridge T. J., Use of the Gram stain in microbiology. Biotech. Histochem. 76, 111–118 (2001). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

