Lung endothelial cell heterogeneity in health and pulmonary vascular disease
- PMID: 39772753
- PMCID: PMC12116231
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00296.2024
Lung endothelial cell heterogeneity in health and pulmonary vascular disease
Abstract
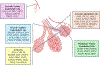
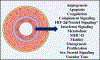
Lung endothelial cells (ECs) are essential for maintaining organ function and homeostasis. Despite sharing some common features with ECs from organ systems, lung ECs exhibit significant heterogeneity in morphology, function, and gene expression. This heterogeneity is increasingly recognized as a key contributor to the development of pulmonary diseases like pulmonary hypertension (PH). In this mini-review, we explore the evolving understanding of lung EC heterogeneity, particularly through the lens of single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) technologies. These advances have provided unprecedented insights into the diverse EC subpopulations, their specific roles, and the disturbances in their homeostatic functions that contribute to PH pathogenesis. In particular, these studies identified novel and functionally distinct cell types such as aerocytes and general capillary ECs that are critical for maintaining lung function in health and disease. In addition, multiple novel pathways and mechanisms have been identified that contribute to aberrant pulmonary vascular remodeling in PH. Emerging techniques like single-nucleus RNA sequencing and spatial transcriptomics have further pushed the field forward by discovering novel disease mediators. As research continues to leverage these advanced techniques, the field is poised to uncover novel EC subtypes and disease mechanisms, paving the way for new therapeutic targets in PH and other lung diseases.
Keywords: angiogenesis; proliferation; pulmonary circulation; pulmonary hypertension; single-cell RNA sequencing.
Figures
References
-
- Huertas A, Guignabert C, Barbera JA, Bartsch P, Bhattacharya J, Bhattacharya S, Bonsignore MR, Dewachter L, Dinh-Xuan AT, Dorfmuller P, Gladwin MT, Humbert M, Kotsimbos T, Vassilakopoulos T, Sanchez O, Savale L, Testa U, and Wilkins MR. Pulmonary vascular endothelium: the orchestra conductor in respiratory diseases: Highlights from basic research to therapy. Eur Respir J 51: 2018. 10.1183/13993003.00745-2017. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 4IPA1275127/American Heart Association (AHA)
- R01 HL077328/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL158507/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- Reuben M. Chernaick Fellowship
- R01HL169509/HHS | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- I01 BX002042/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R01 HL141268/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- Borstein Family Foundation
- R01HL144727/HHS | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- Colorado Pulmonary Vascular Disease Award
- R01 HL170096/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL170096/HHS | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- R01HL158596/HHS | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- R01 HL144727/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL077328/HHS | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- R01 HL169509/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL158596/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL162794/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL141268/HHS | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- R01HL62794/HHS | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

