Hypoxia-inducible factor 2 regulates alveolar regeneration after repetitive injury in three-dimensional cellular and in vivo models
- PMID: 39772774
- PMCID: PMC12051389
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.adk8623
Hypoxia-inducible factor 2 regulates alveolar regeneration after repetitive injury in three-dimensional cellular and in vivo models
Abstract
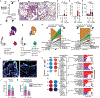
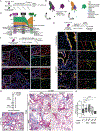
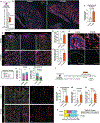
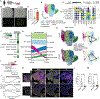
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a progressive interstitial lung disease in which repetitive epithelial injury and incomplete alveolar repair result in accumulation of profibrotic intermediate/transitional "aberrant" epithelial cell states. The mechanisms leading to the emergence and persistence of aberrant epithelial populations in the distal lung remain incompletely understood. By interrogating single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) data from patients with IPF and a mouse model of repeated lung epithelial injury, we identified persistent activation of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) signaling in these aberrant epithelial cells. Using mouse genetic lineage-tracing strategies together with scRNA-seq, we found that these disease-emergent aberrant epithelial cells predominantly arose from airway-derived (Scgb1a1-CreER-traced) progenitors and exhibited transcriptional programs of Hif2a activation. In mice treated with repetitive intratracheal bleomycin, deletion of Epas1 (Hif2a) but not Hif1a, from airway-derived progenitors, or administration of the small-molecule HIF2 inhibitor PT-2385, using both prevention and rescue approaches, attenuated experimental lung fibrosis, reduced the appearance of aberrant epithelial cells, and promoted alveolar repair. In mouse alveolar organoids, genetic or pharmacologic inhibition of Hif2 promoted alveolar differentiation of airway-derived epithelial progenitors. In addition, treatment of human distal lung organoids with PT-2385 increased colony-forming efficiency, enhanced protein and transcriptional markers of alveolar type 2 epithelial cell maturation, and prevented the emergence of aberrant epithelial cells. Together, these studies showed that HIF2 activation drives the emergence of aberrant epithelial populations after repetitive injury and that targeted HIF2 inhibition may represent an effective therapeutic strategy to promote functional alveolar repair in IPF and other interstitial lung diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
JAK reports research grants/contracts from Boehringer Ingelheim and Bristol-Myers-Squibb, and consulting for APIE and ARDA. TSB reports research grants/contracts from Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers-Squibb and Morphic. NEB reports consulting for Deepcell. The other authors report no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- King TE Jr, Bradford WZ, Castro-Bernardini S, Fagan EA, Glaspole I, Glassberg MK, Gorina E, Hopkins PM, Kardatzke D, Lancaster L, Lederer DJ, Nathan SD, Pereira CA, Sahn SA, Sussman R, Swigris JJ, Noble PW, ASCEND Study Group A phase 3 trial of pirfenidone in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med 370, 2083–2092 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Richeldi L, du Bois RM, Raghu G, Azuma A, Brown KK, Costabel U, Cottin V, Flaherty KR, Hansell DM, Inoue Y, Kim DS, Kolb M, Nicholson AG, Noble PW, Selman M, Taniguchi H, Brun M, Le Maulf F, Girard M, Stowasser S, Schlenker-Herceg R, Disse B, Collard HR, INPULSIS Trial Investigators, Efficacy and safety of nintedanib in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med 370, 2071–2082 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Lederer DJ, Martinez FJ, Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med 378, 1811–1823 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Seibold MA, Wise AL, Speer MC, Steele MP, Brown KK, Loyd JE, Fingerlin TE, Zhang W, Gudmundsson G, Groshong SD, Evans CM, Garantziotis S, Adler KB, Dickey BF, du Bois RM, Yang IV, Herron A, Kervitsky D, Talbert JL, Markin C, Park J, Crews AL, Slifer SH, Auerbach S, Roy MG, Lin J, Hennessy CE, Schwarz MI, Schwartz DA, A common MUC5B promoter polymorphism and pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med 364, 1503–1512 (2011). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Thomas AQ, Lane K, Phillips J 3rd, Prince M, Markin C, Speer M, Schwartz DA, Gaddipati R, Marney A, Johnson J, Roberts R, Haines J, Stahlman M, Loyd JE, Heterozygosity for a surfactant protein C gene mutation associated with usual interstitial pneumonitis and cellular nonspecific interstitial pneumonitis in one kindred. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med 165, 1322–1328 (2002). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

