Limnospira (Cyanobacteria) chemical fingerprint reveals local molecular adaptation
- PMID: 39772964
- PMCID: PMC11792457
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.01901-24
Limnospira (Cyanobacteria) chemical fingerprint reveals local molecular adaptation
Abstract
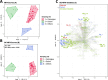
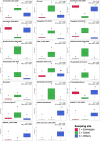
Limnospira can colonize a wide variety of environments (e.g., freshwater, brackish, alkaline, or alkaline-saline water) and develop dominant and even permanent blooms that overshadow and limit the diversity of adjacent phototrophs, especially in alkaline and saline environments. Previous phylogenomic analysis of Limnospira allowed us to distinguish two major phylogenetic clades (I and II) but failed to clearly segregate strains according to their respective habitats in terms of salinity or biogeography. In the present work, we attempted to determine whether Limnospira displays metabolic signatures specific to its different habitats, particularly brackish and alkaline-saline ecosystems. The impact of accessory gene repertoires on respective chemical adaptations was also determined. In complement of our previous phylogenomic investigation of Limnospira (Roussel et al., 2023), we develop a specific analysis of the metabolomic diversity of 93 strains of Limnospira, grown under standardized lab culture conditions. Overall, this original work showed distinct chemical fingerprints that were correlated with the respective biogeographic origins of the strains. The molecules that most distinguished the different Limnospira geographic groups were sugars, lipids, peptides, photosynthetic pigments, and antioxidants. Interestingly, these molecular enrichments might represent consequent adaptations to conditions of salinity, light, and oxidative stress in their respective sampling environments. Although the genes specifically involved in the production of these components remain unknown, we hypothesized that within extreme environments, such as those colonized by Limnospira, a large set of flexible genes could support the production of peculiar metabolite sets providing remarkable adaptations to specific local environmental conditions.
Importance: Limnospira are ubiquitous cyanobacteria with remarkable adaptive strategies allowing them to colonize and dominate a wide range of alkaline-saline environments worldwide. Phylogenomic analysis of Limnospira revealed two distinct major phylogenetic clades but failed to clearly segregate strains according to their habitats in terms of salinity or biogeography. We hypothesized that the genes found within this variable portion of the genome of these clades could be involved in the adaptation of Limnospira to local environmental conditions. In the present paper, we attempted to determine whether Limnospira displayed metabolic signatures specific to its different habitats. We also sought to understand the impact of the accessory gene repertoire on respective chemical adaptations.
Keywords: adaptation; cyanobacteria; genomics; metabolomics; micro-diversity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Reynolds CS. 2006. The ecology of phytoplankton. Cambridge University Press.
-
- Whitton BA, ed. 2012. Ecology of cyanobacteria II: their diversity in space and time. Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht.
-
- Whitton BA, Potts M, eds. 2007. The ecology of cyanobacteria: their diversity in time and space. The Netherlands, Springer Science & Business Media, Dordrecht.
-
- Leflaive J, Ten‐hage L. 2007. Algal and cyanobacterial secondary metabolites in freshwaters: a comparison of allelopathic compounds and toxins. Freshw Biol 52:199–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2427.2006.01689.x - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

