Short-term WB-EMS in Cancer Patients: Positive Effects After 2 Weeks of Exercise-A Single-arm Trial
- PMID: 39773015
- PMCID: PMC11705350
- DOI: 10.1177/15347354241304415
Short-term WB-EMS in Cancer Patients: Positive Effects After 2 Weeks of Exercise-A Single-arm Trial
Abstract
Context: Due to therapeutic side effects and physical weakness, patients are not always able to carry out strenuous and lengthy exercises. Hence, this study investigated the effectiveness and feasibility of a short-term Whole-body electromyostimulation (WB-EMS) for oncological patients during and after anticancer treatment. The primary aim was to ensure the feasibility of WB-EMS training. Furthermore, the effects of WB-EMS training were investigated over a period of 2 weeks on parameters such as quality of life, body composition and physical performance.
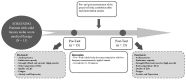
Method: Thirteen cancer patients with different diagnosis, disease stages and treatment state were included. They participated in supervised WB-EMS sessions 4 times over a 2-week period. Physical functioning, body composition, depression, fatigue, and quality of life were measured before and after the intervention period. Moreover, a pre-post measurement of the patients' perceived body constitution was conducted in every exercise session.
Results: All included patients (n = 13) were able to complete the 4 WB-EMS sessions. At the end of the 2 weeks, a significant increase of the muscle strength could be observed. Additionally, patients improved their cardiovascular fitness. The body composition analyses showed significant reductions in body lean mass and extracellular water. Muscle mass remained unchanged. Furthermore, patients reported an improved perceived body constitution reduced pain and discomfort following all 4 WB-EMS sessions.
Conclusion: This study suggests that WB-EMS is safe and feasible for cancer patients. Furthermore, it showed that even after 2 weeks, improvements concerning the physical performance and patient-reported outcomes can be achieved. This study indicates benefits of WB-EMS as short-term exercise methode in cancer patients, that could be utelised in fields such as cancer prehabilitation.
Trial registration: This trial has been registered with the ISRCTN-Registry (ISRCTN68069634).
Keywords: feasibility; oncological patients; physical function; strength training; whole-body electromyostimulation.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting InterestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures


References
-
- Cancer today. The Global Cancer Observatory. Published September 21, 2023. Accessed September 21, 2023. https://gco.iarc.fr/today/fact-sheets-cancers
-
- Cancer Tomorrow. Predictions of the future cancer incidence and mortality burden worldwide up until 2040. Published June 27, 2023. Accessed September 21, 2023. https://gco.iarc.fr/tomorrow/en
-
- Robert Koch-Institut. Bericht zum Krebsgeschehen in Deutschland 2016; 2016.
-
- Koutoukidis DA, Land J, Hackshaw A, et al. Fatigue, quality of life and physical fitness following an exercise intervention in multiple myeloma survivors (MASCOT): an exploratory randomised phase 2 trial utilising a modified Zelen design. Br J Cancer. 2020;123:187-195. doi: 10.1038/s41416-020-0866-y - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

