Complement 3a receptor 1 on macrophages and Kupffer cells is not required for the pathogenesis of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease
- PMID: 39773465
- PMCID: PMC11709426
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.100708
Complement 3a receptor 1 on macrophages and Kupffer cells is not required for the pathogenesis of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease
Abstract
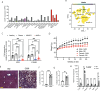
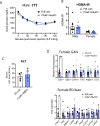
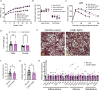
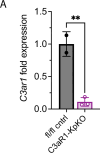
Together with obesity and type 2 diabetes, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is a growing global epidemic. Activation of the complement system and infiltration of macrophages has been linked to progression of metabolic liver disease. The role of complement receptors in macrophage activation and recruitment in MASLD remains poorly understood. In human and mouse, C3AR1 in the liver is expressed primarily in Kupffer cells, but is downregulated in humans with MASLD compared to obese controls. To test the role of complement 3a receptor (C3aR1) on macrophages and liver resident macrophages in MASLD, we generated mice deficient in C3aR1 on all macrophages (C3aR1-MφKO) or specifically in liver Kupffer cells (C3aR1-KpKO) and subjected them to a model of metabolic steatotic liver disease. We show that macrophages account for the vast majority of C3ar1 expression in the liver. Overall, C3aR1-MφKO and C3aR1-KpKO mice have similar body weight gain without significant alterations in glucose homeostasis, hepatic steatosis and fibrosis, compared to controls on a MASLD-inducing diet. This study demonstrates that C3aR1 deletion in macrophages or Kupffer cells, the predominant liver cell type expressing C3ar1, has no significant effect on liver steatosis, inflammation or fibrosis in a dietary MASLD model.
Keywords: C3ar1; fatty liver disease; human; immunology; inflammation; kupffer cells; macrophages; medicine; metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; mouse; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
© 2024, Homan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
EH, AG, AR, MJ, OS, EC, RP, LS, JL No competing interests declared
Figures


Update of
-
Complement 3a Receptor 1 on Macrophages and Kupffer cells is not required for the Pathogenesis of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 9:2024.06.26.24309550. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.26.24309550. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: Elife. 2025 Jan 08;13:RP100708. doi: 10.7554/eLife.100708. PMID: 38978661 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Boland ML, Oró D, Tølbøl KS, Thrane ST, Nielsen JC, Cohen TS, Tabor DE, Fernandes F, Tovchigrechko A, Veidal SS, Warrener P, Sellman BR, Jelsing J, Feigh M, Vrang N, Trevaskis JL, Hansen HH. Towards a standard diet-induced and biopsy-confirmed mouse model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Impact of dietary fat source. World Journal of Gastroenterology. 2019;25:4904–4920. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i33.4904. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Duell PB, Welty FK, Miller M, Chait A, Hammond G, Ahmad Z, Cohen DE, Horton JD, Pressman GS, Toth PP. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and cardiovascular risk: a scientific statement from the american heart association. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 2022;42:e168–e185. doi: 10.1161/ATV.0000000000000153. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

