Targeted inhibition of Aurora kinase A promotes immune checkpoint inhibition efficacy in human papillomavirus-driven cancers
- PMID: 39773561
- PMCID: PMC11749607
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2024-009316
Targeted inhibition of Aurora kinase A promotes immune checkpoint inhibition efficacy in human papillomavirus-driven cancers
Abstract
Background: Human papillomavirus (HPV)-driven cancers include head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and cervical cancer and represent approximately 5% of all cancer cases worldwide. Standard-of-care chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) are associated with adverse effects and limited responses in patients with HPV-driven cancers. The integration of targeted therapies with ICIs may improve outcomes. In a previous study, we demonstrated that Aurora kinase A (AURKA, Aurora A) inhibitors lead to apoptosis of human HPV-positive cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Here, we explored the potential of Aurora A inhibition to enhance response to ICIs in immune-competent preclinical models of HPV-driven cancers.
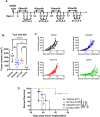
Methods: We assessed the induction of apoptosis, DNA damage, and immunogenic cell death (ICD) in response to treatment with the Aurora A inhibitor alisertib in vitro and antitumor efficacy of alisertib as a monotherapy and in combination with ICIs that inhibit programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) or cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) in murine HPV-positive immune-competent tumor models. In each treatment group, we determined the tumor growth kinetics and long-term survival and assessed the tumor immune microenvironment using polychromatic flow cytometry.
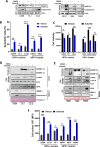
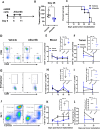
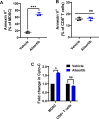
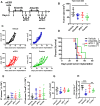
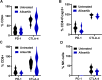
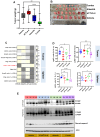
Results: Aurora A inhibition induced apoptosis, DNA damage, and ICD in vitro in multiple human and murine HPV-positive cancer cell lines. Importantly, Aurora A inhibition induced selective apoptotic depletion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs). In vivo experiments demonstrated that the combination of alisertib with ICIs, specifically anti-CTLA4, resulted in improved survival outcomes by altering the tumor immune microenvironment. This combination enhanced CD8 T-cell infiltration and decreased the frequencies of MDSCs, whereas neither alisertib nor ICIs (anti-PD-1/anti-CTLA-4) alone showed such effects.
Conclusion: Our study establishes the potential of Aurora A inhibition to sensitize HPV-positive tumors to ICIs, specifically anti-CTLA-4 treatment. This combination strategy resulted in enhanced antitumor efficacy, driven by systemic and intratumoral increases in CD8 T-cell responses and reduced immunosuppressive cell populations, specifically MDSCs. These findings offer insights into the synergistic effects of Aurora A inhibition and ICIs and argue for further investigation and optimization of this combination approach in HPV-driven cancers.
Keywords: Head and Neck Cancer; Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor; Immunotherapy; Myeloid-derived suppressor cell - MDSC; Viral-specific T cells.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: FMJ and JKS have received research funding from Takeda Pharmaceuticals. All other authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Burtness B, Harrington KJ, Greil R, et al. Pembrolizumab alone or with chemotherapy versus cetuximab with chemotherapy for recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (KEYNOTE-048): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet. 2019;394:1915–28. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32591-7. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
