Extracellular vesicle-mediated approaches for the diagnosis and therapy of MASLD: current advances and future prospective
- PMID: 39773634
- PMCID: PMC11705780
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-024-02396-3
Extracellular vesicle-mediated approaches for the diagnosis and therapy of MASLD: current advances and future prospective
Abstract
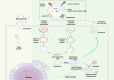
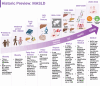
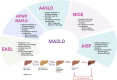
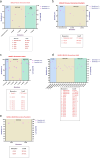
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is an asymptomatic, multifaceted condition often associated with various risk factors, including fatigue, obesity, insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, and sleep apnea. The increasing burden of MASLD underscores the critical need for early diagnosis and effective therapies. Owing to the lack of efficient therapies for MASLD, early diagnosis is crucial. Consequently, noninvasive biomarkers and imaging techniques are essential for analyzing disease risk and play a pivotal role in the global diagnostic process. The use of extracellular vesicles has emerged as promising for early diagnosis and therapy of various liver ailments. Herein, a comprehensive summary of the current diagnostic modalities for MASLD is presented, highlighting their advantages and limitations while exploring the potential of extracellular vesicles (EVs) as innovative diagnostic and therapeutic tools for MASLD. With this aim, this review emphasizes an in-depth understanding of the origin of EVs and the pathophysiological alterations of these ectosomes and exosomes in various liver diseases. This review also explores the therapeutic potential of EVs as key components in the future management of liver disease. The dual role of EVs as biomarkers and their therapeutic utility in MASLD essentially highlights their clinical integration to improve MASLD diagnosis and treatment. While EV-based therapies are still in their early stages of development and require substantial research to increase their therapeutic value before they can be used clinically, the diagnostic application of EVs has been extensively explored. Moving forward, developing diagnostic devices leveraging EVs will be crucial in advancing MASLD diagnosis. Thus, the literature summarized provides suitable grounds for clinicians and researchers to explore EVs for devising diagnostic and treatment strategies for MASLD.
Keywords: Biomarker; Extracellular vesicles; Liver diseases; Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; Targeted therapy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

