Effectiveness of Using a Digital Wearable Plantar Pressure Device to Detect Muscle Fatigue: Within-Subject, Repeated Measures Experimental Design
- PMID: 39773695
- PMCID: PMC11731697
- DOI: 10.2196/65578
Effectiveness of Using a Digital Wearable Plantar Pressure Device to Detect Muscle Fatigue: Within-Subject, Repeated Measures Experimental Design
Abstract
Background: Muscle fatigue, characterized by reduced force generation during repetitive contractions, impacts older adults doing daily activities and athletes during sports activities. While various sensors detect muscle fatigue via muscle activity, biochemical markers, and kinematic parameters, a real-time wearable solution with high usability remains limited. Plantar pressure monitoring detects muscle fatigue through foot loading changes, seamlessly integrating into footwear to improve the usability and compliance for home-based monitoring.
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the effects of muscle fatigue on plantar pressure measurements using a self-developed wearable plantar pressure system.
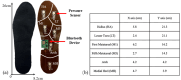
Methods: Twelve healthy participants completed a 5-minute calf muscle fatigue protocol. The plantar pressures and surface electromyography (sEMG) activity of the gastrocnemius muscles were recorded before and after exercise. The plantar pressures at 6 regions and the median frequency (MDF) of sEMG were analyzed to quantify fatigue.
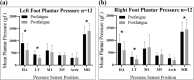
Results: The self-developed foot pressure system showed a significant decrease in plantar pressure peak values at the heel of the left (P=.003) and right feet (P=.001) and at the lateral toe of the left (P=.001) and right feet (P=.026). A significant increase was observed at the metatarsal head of both the left foot (P=.001) and the right foot (P=.017). The MDF of sEMG signals significantly decreased in the left (P=.001) and right gastrocnemius (P<.001).
Conclusions: Plantar pressure changes and sEMG signals effectively detect gastrocnemius muscle fatigue using the proposed wearable system, supporting the development of a wearable solution for detecting muscle fatigue suitable for home-use.
Keywords: home-based monitoring; muscle fatigue; plantar pressure sensors; wearable devices.
© Fu-Yu Chen, Tzu-Yao Lin, Yi-Cheng Huang, Evina Widianawati. Originally published in JMIR Human Factors (https://humanfactors.jmir.org).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Do somatosensory conditions from the foot and ankle affect postural responses to plantar-flexor muscles fatigue during bipedal quiet stance?Gait Posture. 2012 May;36(1):16-9. doi: 10.1016/j.gaitpost.2011.10.361. Epub 2012 Mar 31. Gait Posture. 2012. PMID: 22465704
-
Effects of various walking intensities on leg muscle fatigue and plantar pressure distributions.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021 Sep 27;22(1):831. doi: 10.1186/s12891-021-04705-8. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021. PMID: 34579699 Free PMC article.
-
Plantar Pressure Variability and Asymmetry in Elderly Performing 60-Minute Treadmill Brisk-Walking: Paving the Way towards Fatigue-Induced Instability Assessment Using Wearable In-Shoe Pressure Sensors.Sensors (Basel). 2021 May 6;21(9):3217. doi: 10.3390/s21093217. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34066398 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of prolonged brisk walking induced lower limb muscle fatigue on the changes of gait parameters in older adults.Gait Posture. 2023 Mar;101:145-153. doi: 10.1016/j.gaitpost.2023.02.010. Epub 2023 Feb 15. Gait Posture. 2023. PMID: 36841121
-
Advancements in Textile-Based sEMG Sensors for Muscle Fatigue Detection: A Journey from Material Evolution to Technological Integration.ACS Sens. 2024 Sep 27;9(9):4380-4401. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.4c00604. Epub 2024 Sep 6. ACS Sens. 2024. PMID: 39240819 Review.
References
-
- Sarshin A, Mohammadi S, Shahraba HBP, Sedigh M. The effects of functional fatique on dynamic postural control of badminton players. Biol of Exerc. 2011;7(2):25–34. doi: 10.4127/jbe.2011.0047. doi. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

