The interplay of exercise and green tea: a new road in cancer therapy
- PMID: 39773739
- PMCID: PMC11705833
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-024-03632-7
The interplay of exercise and green tea: a new road in cancer therapy
Abstract
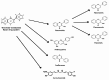
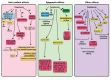
Exercise is one of the most important activities for every individual due to its proven health beneficials. Several investigations have highlighted the advantageous impacts of aerobic exercise, largely attributed to its capacity to enhance the body's capability to defend against threats against oxidative stress. The information currently accessible suggests that adding regular aerobic exercise to a daily routine greatly decreases the chances of developing serious cancer and passing away. An unevenness in the levels of free radicals and the body's antioxidant defenses, made up of enzyme and non-enzyme antioxidants, results in oxidative pressure. Generally, an imbalance in the levels of oxidative stress triggers the creation of harmful reactive oxygen or nitrogen compounds, causing the development or progression of numerous ailments, including cancer. The equilibrium between pro-oxidant and antioxidant substances is a direct indicator of this imbalance. Green tea and its derivatives are rich sources of bioactive substances such as flavonoids and polyphenols which possess antioxidant abilities. Moreover, modulation of epigenetic targets as well as inflammatory pathways including ERK1/2 and NF-κB are other proposed mechanisms for its antioxidant activity. Recent studies demonstrate the promise of green tea as an antioxidant, showing its ability to decrease the likelihood of developing cancer by impacting actions like cell growth, blood vessel formation, and spread of cancer cells. This summary will concentrate on the complex network of different pathways related to physical activity and consumption of green tea. In particular, the focus of this research will be on examining how oxidative stress contributes to health and investigating the potential antioxidant properties of green tea, and the interconnected relationship between exercise and green tea in the treatment of cancer. Elucidation of these different pathways would help scientists for development of better therapeutic targets and further increase of current anticancer agents efficiency.
Keywords: Cancer; Exercise; Green tea.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: None . Consent for publication: None . Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

