Education strategies are the most commonly used in pediatric rehabilitation implementation research: a scoping review
- PMID: 39773757
- PMCID: PMC11706032
- DOI: 10.1186/s43058-024-00690-w
Education strategies are the most commonly used in pediatric rehabilitation implementation research: a scoping review
Erratum in
-
Correction: Education strategies are the most commonly used in pediatric rehabilitation implementation research: a scoping review.Implement Sci Commun. 2025 Jan 31;6(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s43058-025-00700-5. Implement Sci Commun. 2025. PMID: 39891209 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Approximately one in six children has a disability, and effective, evidence-based rehabilitation can ameliorate the impact of these conditions over the lifespan. However, implementing interventions in real-world settings remains a challenge. This scoping review aimed to summarize the characteristics, implementation strategies, and outcomes of implementation studies in pediatric rehabilitation.
Methods: A comprehensive search was conducted in PubMed/MEDLINE, EMBASE, CINAHL, SCOPUS, and Web of Science from the database inception to December 2, 2022. Studies testing implementation strategies in pediatric rehabilitation interventions were included. Data extracted included study characteristics (e.g., country, intervention type, field of rehabilitation), implementation strategies characterized using the Expert Recommendations for Implementing Change taxonomy, and outcomes based on the Implementation Outcomes Framework.
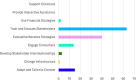
Results: Of the 11,740 studies identified, 44 met the inclusion criteria. Most studies were conducted in the United States (n = 15, 34%) or Canada (n = 10, 23%) and used a mixed-methods design (n = 13, 30%). Interventions primarily targeted motor skills (n = 19, 43%) and were conducted in outpatient settings (n = 14, 32%) or homes (n = 11, 23%). The most commonly used implementation strategies were "train and educate key informant" (n = 21, 48%) and "use evaluative/iterative strategies" (n = 19, 43%). Feasibility (n = 19, 43%) and acceptability (n = 16, 36%) were the most frequently targeted implementation outcomes.
Conclusions: Reporting implementation strategies and outcomes in pediatric rehabilitation studies is limited and highly variable. Most strategies focused on developing and sharing educational materials, while administrative and systems-level interventions were largely absent. Standardized documentation of implementation strategies and outcomes could advance the field's understanding of the effective development of interventions designed for implementation, encouraging faster uptake of effective interventions.
Keywords: Implementation; Occupational therapy; Pediatrics; Physical therapy; Rehabilitation; Speech language pathology.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Elvin Geng, one of the authors of this paper, is an associate editor for Implementation Science Communications Journal.
Figures
References
-
- Kaye HS. Trends in disability rates in the United States, 1970–1994. US Department of Education, National Institute on Disability and Rehabilitation Research (NIDRR); 1996. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous