Neuronal CD59 isoforms IRIS-1 and IRIS-2 as regulators of neurotransmitter release with implications for Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 39773760
- PMCID: PMC11705862
- DOI: 10.1186/s13195-024-01660-z
Neuronal CD59 isoforms IRIS-1 and IRIS-2 as regulators of neurotransmitter release with implications for Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
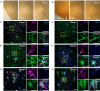
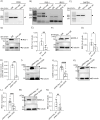
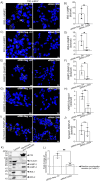
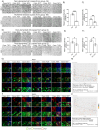
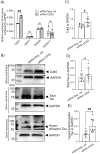
We have previously demonstrated that the intracellular, non-GPI anchored CD59 isoforms IRIS-1 and IRIS-2 (Isoforms Rescuing Insulin Secretion 1 and 2) are necessary for insulin secretion from pancreatic β-cells. While investigating their expression across human tissues, we identified IRIS-1 and IRIS-2 mRNA in the human brain, though their protein expression and function remained unclear. This study shows the presence of both IRIS-1 and 2 proteins in the human brain, specifically in neurons and astrocytes. In the neuroblastoma cell line (SH-SY5Y), both isoforms are intracellular, and their expression increases upon differentiation into mature neurons. Silencing IRIS-1 and 2 in SH-SY5Y cells reduces the SNARE complex formation, essential for synaptic vesicle exocytosis, leading to a reduction in noradrenaline secretion. Notably, we observed diminished expression of neuronal IRIS-1 and 2 in patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD) and non-demented individuals with type 2 diabetes (T2D). In SH-SY5Y cells, knockdown of all isoforms of CD59 including IRIS-1 and 2 not only elevates phosphorylated tau but also increases cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (CDK5) expression, known promoter of hyperphosphorylation and accumulation of tau, a key pathological feature of AD. Additionally, we found that prolonged exposure to high glucose or cytokines markedly reduces the expression of IRIS-1 and 2 in SH-SY5Y cells, suggesting a link between AD pathology and metabolic stress through modulation of these isoforms.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; CD59; IRIS-1; IRIS-2; Intracellular complement; Neurotransmitters release; SNARE; Tau hyperphosphorylation; Type 2 diabetes.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Informed consents for the use of brain tissue, plasma, and clinical data for research purposes were obtained from all subjects or their legal representatives in accordance with the International Declaration of Helsinki [15]. The tissue collection protocols were approved by the medical ethics committee of VU medical Centre in Amsterdam, the Netherlands and the Swedish Ethical Review Authority approved the study (Dnr 2016/155, 2017/717). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Financial disclosures: The authors declare no financial disclosures.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

