Relationship between staff experience and patient outcomes in hospital settings: an overview of reviews
- PMID: 39773811
- PMCID: PMC11749438
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-091942
Relationship between staff experience and patient outcomes in hospital settings: an overview of reviews
Abstract
Objectives: This review aimed to investigate the relationship between staff experience and patient health and experience outcomes in hospital inpatient settings.
Design: Systematic review of reviews.
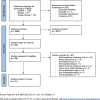
Methods: Searches were performed in Medline (OVID), CINAHL and Google Scholar using key terms from relevant review articles. The search was conducted on 28 August 2023. Inclusion criteria were systematic or narrative reviews in English from 2020 onwards, focusing on inpatients in hospital and related tertiary care facilities, examining the relationship between staff experience and patient outcomes. A review of reviews approach was used, with broad definitions for staff experience (eg, hospital culture, stress and burnout) and patient outcomes (eg, adverse events and patient experience). Independent screening and quality appraisal were conducted by two researchers. An evidence map of links between staff experience and patient outcomes was created. The methodological quality of systematic reviews was assessed using the AMSTAR 2 tool and narrative reviews with the SANRA tool.
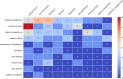
Results: From 2365 citations, 21 reviews (18 systematic, 3 narrative) were included. Review quality ranged from moderate to high. Mapping revealed 66 associations between staff experience and patient outcomes. Common associations included burnout, stress and fatigue with adverse events (six reviews); communication with patient satisfaction (four reviews) and teamwork with patient satisfaction (four reviews).
Conclusions: Staff burnout, teamwork and communication practices directly impact adverse events and patient satisfaction. These findings guide hospital managers and clinicians in improving health service policies and practices. Further research is needed to strengthen the evidence base.
Keywords: Hospitals; Patient Reported Outcome Measures; Patient Satisfaction; Systematic Review; Work Satisfaction.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Seidu S, Opoku Mensah A, Issau K, et al. Does organisational culture determine performance differentials in the hospitality industry? Evidence from the hotel industry. JHTI. 2022;5:535–52. doi: 10.1108/JHTI-11-2020-0208. - DOI
-
- Coelho C, Mojtahedi M, Kabirifar K, et al. Influence of Organisational Culture on Total Quality Management Implementation in the Australian Construction Industry. Bld. 2022;12:496. doi: 10.3390/buildings12040496. - DOI
-
- RSM UK . United Kingdom; 2023. [15-Aug-2023]. Rapid literature review: safety culture.https://www.cqc.org.uk/about-us/transparency/external-reports-research/r... Available. accessed.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources