Formulation development and evaluation, in silico PBPK modeling and in vivo pharmacodynamic studies of clozapine matrix type transdermal patches
- PMID: 39774012
- PMCID: PMC11707343
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-81918-6
Formulation development and evaluation, in silico PBPK modeling and in vivo pharmacodynamic studies of clozapine matrix type transdermal patches
Abstract
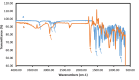
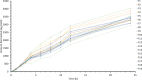
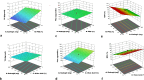
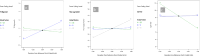
Clozapine is a potent serotonin receptor antagonist and commonly used for the treatment of Schizophrenia. The study aimed to develop and optimize the transdermal matrix patch of clozapine. A 3-level, 3-factor Central Composite Design was applied to examine and validate the impact of various formulation variables, Eudragit, PEG, and oleic acid on in vitro drug release, flux, and tensile strength (TS). Different formulation characteristics were studied in terms of physico-chemical characterization, Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR), Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC), drug release performance, and in vitro permeability. The numerical and graphical optimization was based on the desirability function and the optimized formulation obtained from the polynomial equation was further validated and evaluated for the targeted critical attributes. The optimized patch was further evaluated for skin irritation, in vivo pharmacodynamics, in silico prediction, and simulation using the GastroPlus TCAT® model and stability. The experimental results of the optimized formulation, such as tensile strength 1.220 kg/cm2, flux 147.376 μg/cm2/h and Q24 94.874%, showed similarity with the values predicted by numerical and graphical optimization. In vivo Neuro-pharmacological studies showed that the results were comparable to the standard. The Cmax, Tmax, AUCt, and AUCinf were predicted as 38.396 ng/mL, 28.960 h, 1625.500 ng-h/mL, and 1175.700 ng-h/mL for a 50 mg patch. No skin irritation was found for the optimized transdermal patch as per the Draize score method. The shelf life of the optimized formulation was 30.41 months under accelerated conditions. The study showed that the matrix-type transdermal patch of clozapine can be used for the management of schizophrenia in terms of improved patient compliance.
Keywords: Central composite design; In vitro; In vivo; PBPK; Permeation enhancers, in silico; Transdermal drug delivery.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Yang, Z. et al. Once-daily versus divided dosing regimens of clozapine: A cross-sectional study in Singapore. Schizophr. Res.10.1016/j.schres.2023.10.001 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Pharma, M. Clozapine Prescribing Information (2021).
-
- Manjunath, K. & Venkateswarlu, V. Pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution and bioavailability of clozapine solid lipid nanoparticles after intravenous and intraduodenal administration. J. Control. Release107, 215–228. 10.1016/j.jconrel.2005.06.006 (2005). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

