CD36 in liver diseases
- PMID: 39774047
- PMCID: PMC11717518
- DOI: 10.1097/HC9.0000000000000623
CD36 in liver diseases
Abstract
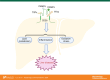
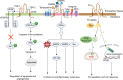
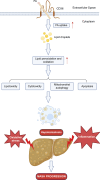
Cluster of differentiation 36 (CD36) is a transmembrane glycoprotein with the ability to bind to multiple ligands and perform diverse functions. Through the recognition of long-chain fatty acids, proteins containing thrombospondin structural homology repeat domains such as thrombospondin-1, and molecules with molecular structures consistent with danger- or pathogen-associated molecular patterns, CD36 participates in various physiological and pathological processes of the body. CD36 is widely expressed in various cell types, including hepatocytes and KCs in the liver, where it plays a pivotal role in lipid metabolism, inflammation, and oxidative stress. Accumulating evidence suggests that CD36 plays a complex role in the development of nonalcoholic simple fatty liver disease and NASH and contributes to the pathogenesis of inflammatory liver injury, hepatitis B/hepatitis C, liver fibrosis, and liver cancer. This review summarizes the current understanding of the structural properties, expression patterns, and functional mechanisms of CD36 in the context of liver pathophysiology. Furthermore, the potential of CD36 as a therapeutic target for the prevention and treatment of liver diseases is highlighted.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts to report.
Figures
References
-
- Glatz JFC, Heather LC, Luiken J. CD36 as a gatekeeper of myocardial lipid metabolism and therapeutic target for metabolic disease. Physiol Rev. 2024;104:727–764. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

